Introduction
Public spaces alongside urban and rural infrastructure depend on street lights for two vital functions: safety protection and traffic navigation. Modern street lighting has transformed since ancient times through the adoption of modern LED technology which emphasizes energy-efficient, sustainable, and smart solutions. Each street lighting technology, including traditional incandescent lamps, high-pressure sodium, and metal halide, and modern LED street lights has its unique purpose. LED street lights have a longer lifespan compared to traditional options, making them more efficient in the long run. Knowledge of different lighting technologies enables the proper selection of road lighting systems for residential zones, parking areas, and public domains. The guide provides details about different street light types together with their operational functions and essential selection criteria.
Types of Street Lights: A Detailed Classification and How They work
Several specific categories exist for street lights that display unique properties alongside favorable aspects and particular uses. The selection of suitable lighting solutions depends on understanding different classifications. The following analysis focuses on examining street light categories through the evaluation of their unique features together with their advantages and particular usage applications.
Traditional Street Lights
Incandescent Street Lights
Description: Incandescent street lights represent among the earliest electric street lighting technologies that exist today. The device functions by enabling electricity to pass through a tungsten filament inside a glass bulb containing inert gas. The filament heats up through the electric current flow until it produces light. The basic operating principle behind traditional lighting technology exists in this straightforward system. The high power requirements and brief operational duration of incandescent bulbs result in lower efficiency than contemporary lighting solutions.
Operating Principle: The operating principle of incandescent street lights involves heating a tungsten filament inside a sealed glass bulb that contains inert gas while an electric current passes through it. The resistance of electricity through the filament causes it to glow while producing visible light. The simplicity of production and low cost of incandescent bulbs does not outweigh their low efficiency and brief operational life which makes them less suitable for modern applications.
Halogen Street Lights
Description: The improved version of incandescent lights exists as halogen street lights. The bulb contains a tungsten filament surrounded by halogen gas. The halogen gas protects the filament from deterioration while simultaneously minimizing bulb blackening to increase both operational duration and light output. The improved performance of halogen lights fails to overcome their high energy consumption and heat generation which reduces their usage in modern applications.
Operating Principle: The operating principle of halogen street lights matches incandescent lights with the inclusion of halogen gas. The presence of halogen gas stops tungsten from building up on the bulb walls, which helps prolong the filament’s life while keeping the bulb clear. These lighting solutions provide better performance than incandescent lights, yet they continue to have energy efficiency and heat production constraints.
Fluorescent Street Lights
Description: The light production process of fluorescent street lights operates through an alternative method. The tubes contain gas and have phosphor coating on their interior walls. An electric current activates the gas which produces ultraviolet light. The phosphor coating transforms the ultraviolet light into visible light. Fluorescent lights surpass incandescent and halogen lights in energy efficiency and operate for extended periods. The operation of these lights needs ballasts to control the current flow yet these components increase their operational complexity.
Operating Principle: The electric current that passes through fluorescent street lights activates the tube gas to produce ultraviolet light. The phosphor coating inside the tube converts ultraviolet light into visible light. These lights provide better efficiency and longer operational life than incandescent and halogen lights yet need ballasts as additional equipment that makes installation and maintenance more complex.
High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Street Lights
Description: Traditional street lighting such as High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) street lights function through electric current passage in a sealed tube containing sodium and mercury gas mixtures. The electric current creates a bright yellowish light when it interacts with sodium vapor. High pressure HPS lights provide both superior energy efficiency and extended operational life, which makes them suitable for urban and highway illumination. These lights produce yellow illumination that reduces color discrimination ability, but their broken bulbs release mercury, which creates environmental hazards and health risks.
Operating Principle: High pressure sodium HPS street lights produce bright yellow light through the process of electric current excitation inside sealed sodium vapor tubes. These lighting devices operate with high efficiency and durability, which makes them appropriate for big-scale installations. The yellowish coloration together with mercury content creates challenges for these lights.
Mercury Vapor Street Lights
Description: The operation of Mercury vapor street lights depends on the excitation of mercury vapor inside a glass tube which results in white blue light production. Mercury vapor street lights once gained popularity because of their efficiency and extended lifespan yet HPS and modern LED lights have become their replacements. The efficiency of Mercury vapor lights falls behind HPS lights while their mercury content presents environmental and health dangers when bulbs break.
Operating Principle: The operation of Mercury vapor street lights generates bluish-white light through electric current stimulation of mercury vapor contained within a glass tube. The widespread use of mercury vapor street lights diminished because they offered less efficiency and contained toxic mercury which made them less desirable than modern safer alternatives.
Energy Efficiency and Performance Comparison
| Type of Light | Energy Efficiency | Performance Metrics | Environmental Impact | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Incandescent Street Lights | Low efficiency; most energy is wasted as heat. | Low lumens per watt (lm/W), lifespan of 1,000 to 2,000 hours. | Increased carbon footprint due to high energy consumption; produces excessive heat. | Simple to produce and inexpensive. | Short lifespan; low energy efficiency; high power consumption. |
| Halogen Street Lights | Higher efficiency than incandescent, but still produces a lot of heat. | Slightly higher lm/W than incandescent, lifespan of 2,000 to 4,000 hours. | Similar to incandescent with high energy consumption and heat generation. | Longer lifespan and better performance than incandescent. | High energy consumption and heat generation; not very suitable for modern applications. |
| Fluorescent Street Lights | More efficient than incandescent and halogen, but needs ballasts. | Higher lm/W ratio, lifespan of 8,000 to 10,000 hours. | Less environmental impact than incandescent or halogen, but still relies on non-renewable energy. | Better energy efficiency and longer lifespan than incandescent and halogen. | Requires ballasts for operation, which increases complexity and cost; still dependent on non-renewable energy. |
| High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lights | High energy efficiency and longer operational life. | High lm/W ratings, lifespan of 10,000 to 24,000 hours. | Energy use is better than incandescent or halogen, but relies on non-renewable energy sources. | Superior energy efficiency and long lifespan. Suitable for large-scale installations and outdoor applications. | Yellow light reduces color discrimination; mercury content in broken bulbs creates health and environmental risks. |
| Mercury Vapor Street Lights | Less efficient than HPS, but once popular for their lifespan. | Low efficiency, lifespan shorter than HPS, produces bluish-white light. | Contains toxic mercury, which creates environmental hazards and health risks if bulbs break. | Longer lifespan compared to incandescent and halogen. | Low efficiency; contains toxic mercury; has been largely replaced by safer alternatives. |
Energy Efficiency: Incandescent and halogen lights waste most electrical energy by turning it into heat instead of visible light since they only produce a small fraction of light output. Fluorescent lights operate with greater efficiency because they transform a higher amount of energy into visible light. HPS lights have proven their efficiency in urban lighting applications because of their superior performance. The efficiency of Mercury vapor lights falls below HPS lights while their bulbs contain toxic mercury that creates environmental and health hazards when they break.
Performance Metrics: Incandescent lights operate with low efficiency because they produce few lumens per watt (lm/W) and survive only between 1,000 to 2,000 hours. The performance of halogen lights includes a lm/W rating which is slightly higher than other options and they operate for 2,000 to 4,000 hours. Fluorescent lights deliver superior performance with an lm/W ratio and operate for 8,000 to 10,000 hours. The performance of HPS lights includes high lm/W ratings combined with a lifespan of 10,000 to 24,000 hours. The combination of low efficiency and short operational life together with toxic mercury content makes mercury vapor lights less desirable than HPS lights. Outdoor lighting options like HPS lights provide a lot of light for extended periods, making them suitable for various applications.
Environmental Impact: Near-daily operations of traditional street light technologies such as incandescent and halogen create increased carbon footprint because they burn more energy while generating excessive heat. Fluorescent and HPS lighting solutions use energy better than other options however they both depend on non-renewable energy supplies. The toxic nature of mercury makes mercury vapor light problematic for the environment. Modern environmental sustainability targets view these lighting solutions unfavorably because of their negative impact on the environment. HPS lights, on the other hand, provide long time service while ensuring better energy efficiency.
Modern Street Lights
LED (Light Emitting Diode) Street Lights
Description: LED street lights represent the cutting-edge and commonly used form of contemporary street illumination. Semiconductor materials in LED technology produce light through electric current transmission which generates photons as energy output. The technological characteristics of LEDs include light efficiency, less power consumption, and lengthy operational life combined with concentrated beam output and minimization of light pollution and power wastage. LEDs provide multiple color temperature options ranging from warm white to cool daylight, which makes them suitable for different applications. LEDs provide a cost-effective solution for lighting needs because they maintain themselves well and exist for extended periods while serving both urban and rural areas.
Operating Principle: The semiconductor material inside LED street lights converts electric current into photons when an electric current flows through it. The light production process maintains high efficiency because it produces less heat energy waste. LEDs direct their light towards specific targets which minimizes both wasted illumination and unwanted light contamination in the environment. These lights work well under various lighting conditions because their temperature settings range from warm to bright daylight illumination.
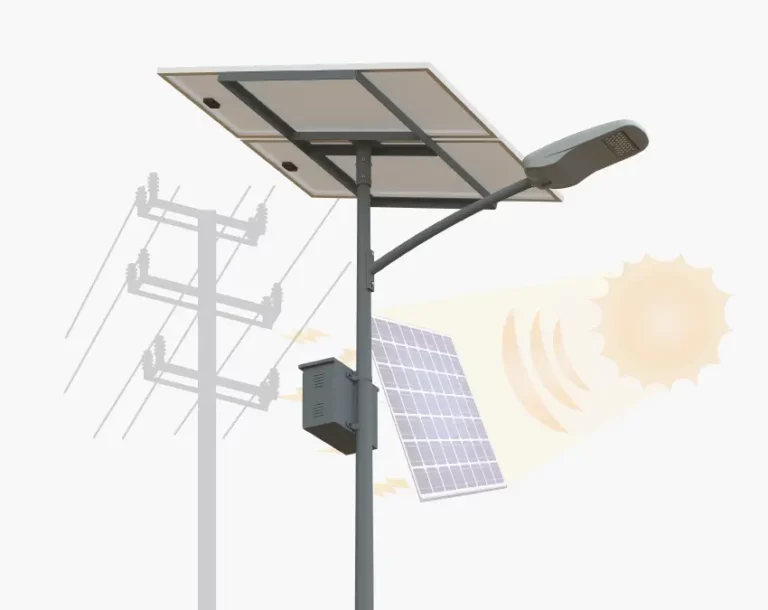
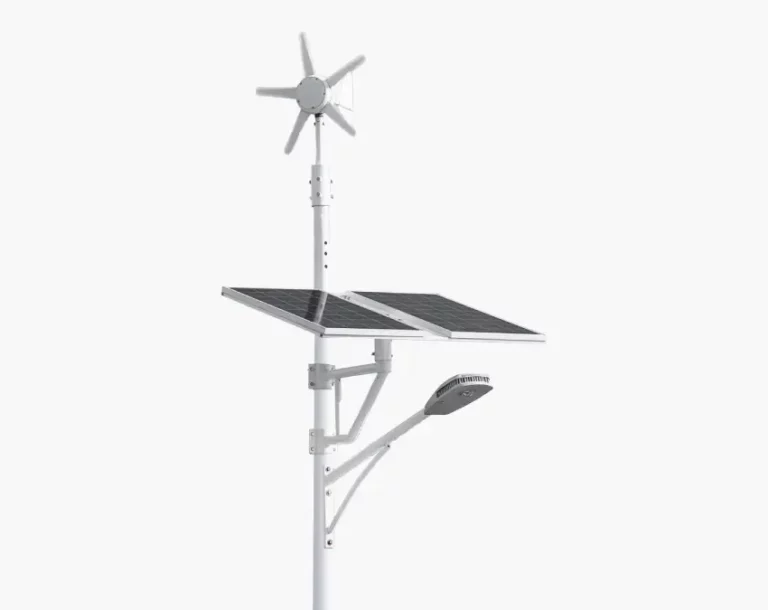
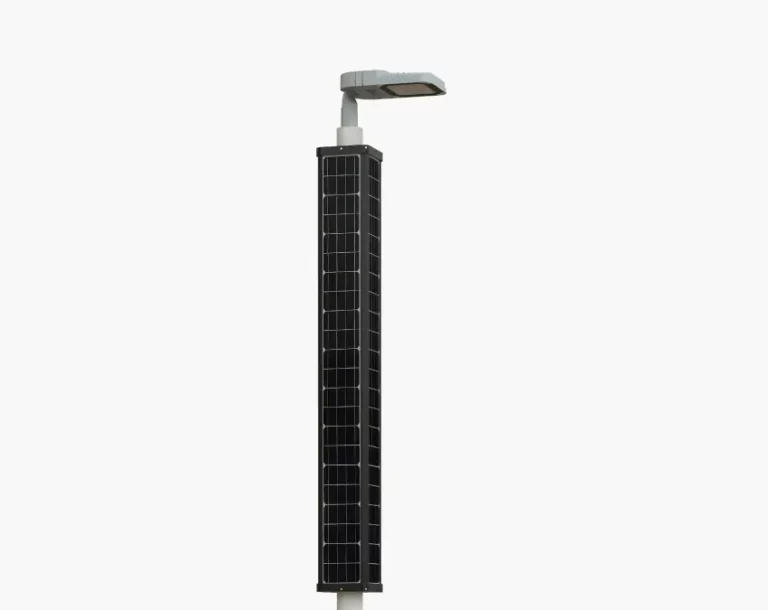
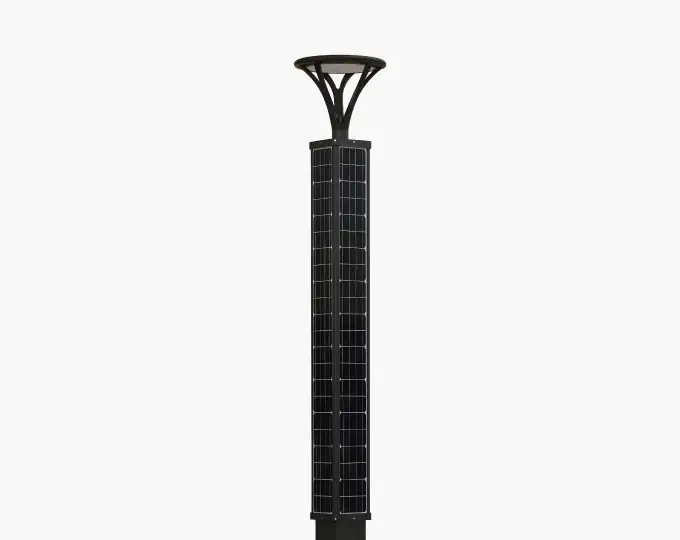
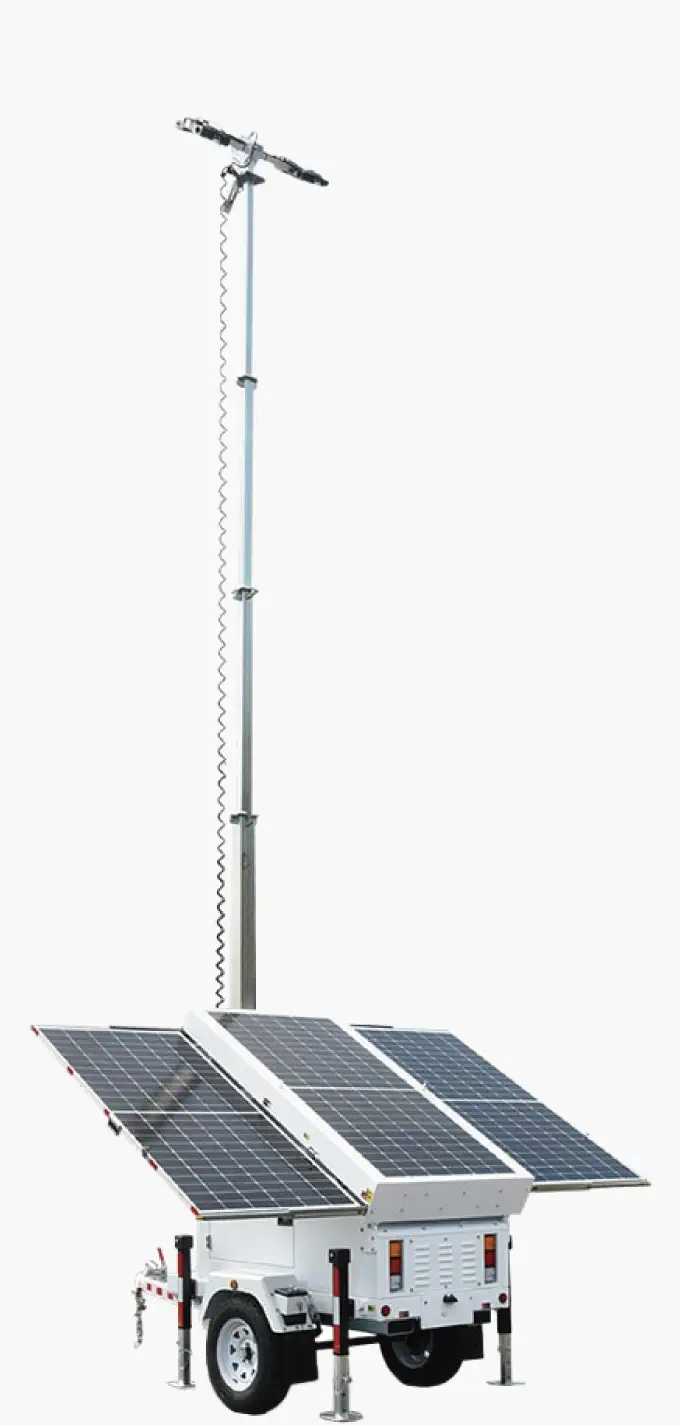
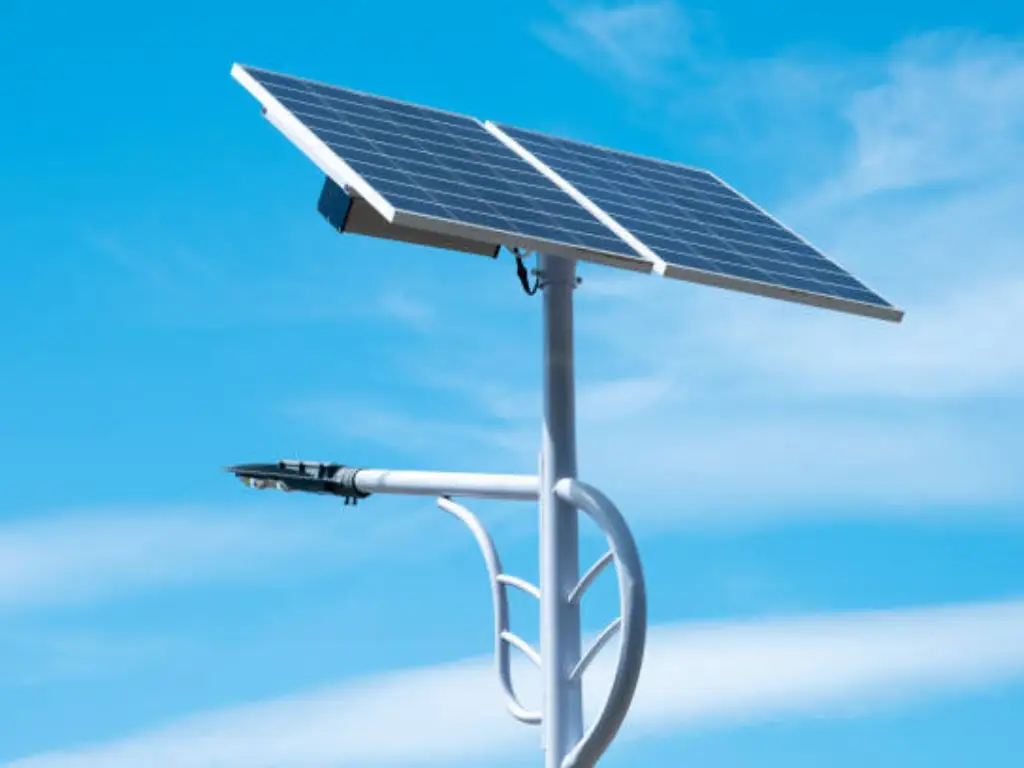
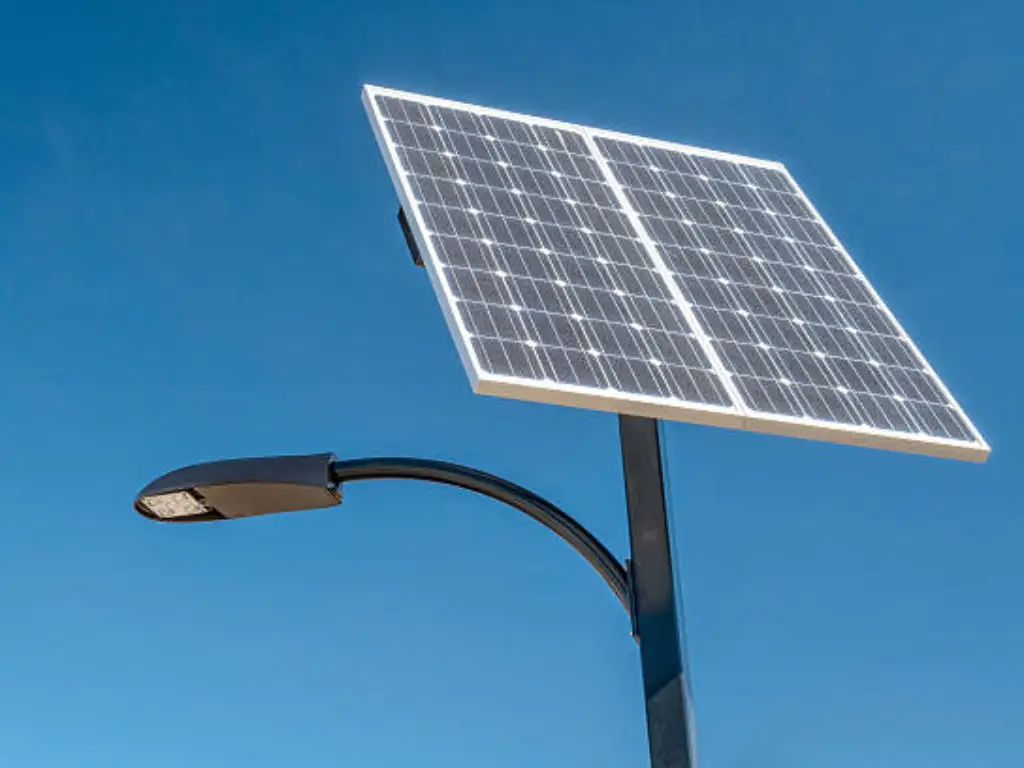
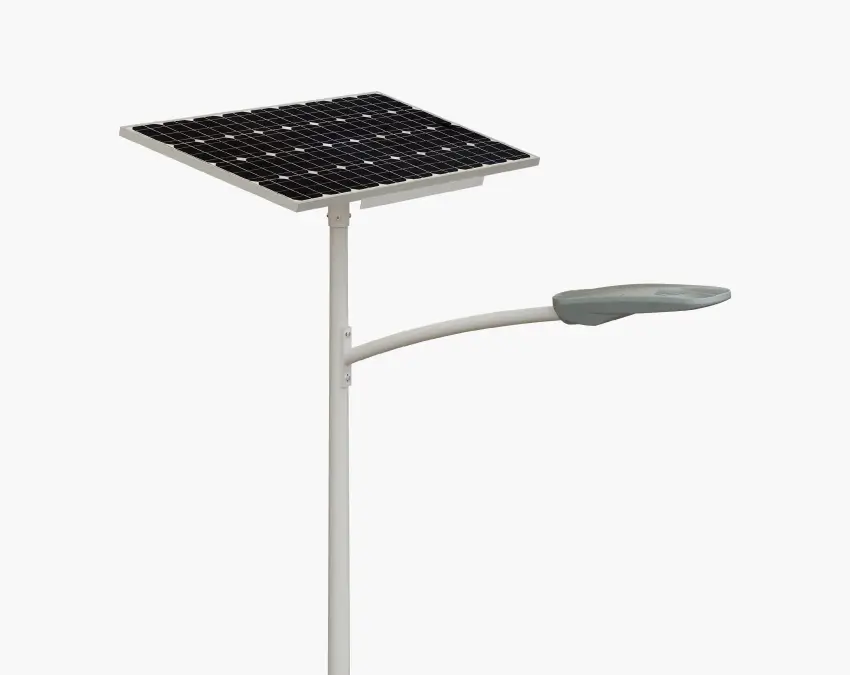
Solar Street Lights
Description: The most efficient street lights are Solar Street Lights. It makes use of solar energy and photovoltaic cells for LED systems, making it one of the most economical options for illuminating streets. Solar street lights charge batteries during the day which light the LEDs at night. Solar street lights are perfect for regions which receive more sunlight as well as for places which do not have sufficient energy sources like remote areas, parks, and regions which are sensitive to ecological disruption. Types of lights used in solar street lighting include LED systems that offer a long lifespan. Contrary to other lights, solar street lights do have some disadvantages such as dependence on weather conditions and an increase in investment when compared to traditional street lights.
Operating Principle: Solar street lights use photovoltaic panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy, which is then stored into batteries. At night, these rechargeable batteries unlock their power and deliver energy to LED lights. The system is effective in renewable energy collection and is an ample source of light in places which do not have access to traditional power sources. While being eco-friendly, considerable solar energy features such as seasonal changes can affect their performance and will require backup systems or larger battery capacities.
Induction Street Lights
Description: Electrodeless lamps known as induction street lights generate light through electromagnetic induction without requiring electrodes. The innovative design structure of these lights increases their operational duration and boosts their performance above conventional lighting systems. Induction street lights serve as dependable lighting solutions for particular applications even though they are less popular than LEDs and solar street lights.
Operating Principle: The operation of induction street lights involves electromagnetic induction which creates light by inducing current in bulb gas to produce excited light emissions. The absence of electrodes in this design extends the product’s operational lifespan. The efficiency and durability of induction street lights have not gained as much popularity as LEDs and solar lights because of their higher initial costs and limited awareness about their advantages.
Smart Street Lights
Description: The highlight of street lighting advancements lies with smart street lights. Smart lights are enabled with sensors, IoT ( Internet of Things) technology, and centralized management systems which facilitate real-time control and monitoring. With the ability to adjust brightness according to light intensity, identify motion, and assess traffic and environmental parameters, these lights are a cut above the rest. These functionalities make them perfect for smart cities or modern urban setups, as they are very efficient in energy consumption.
Operating Principle: Using sensors and IoT technology, smart street lights drastically improve energy consumption while utilising adaptive lighting. Smart lights increase or decrease the brightness depending on the time of day or movement to optimise energy usage. Moreover, they can also collect and relay information to authorities regarding the traffic patterns, the quality of air, or other ecological conditions to assist in the management of the city. Embedding lamp posts with the power to collect and analyse data is a giant leap in the urban infrastructure development.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Comparing Energy Efficiency and Performance Metrics
| Type of Light | Energy Efficiency | Performance Metrics | Environmental Impact | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| LED Street Lights | 70% of energy converted into visible light; highly energy-efficient. | High lm/W rating (up to 100), lifespan of 25,000 to 50,000 hours or more. | Minimal energy consumption; eco-friendly; reduces carbon footprint. | Extremely efficient; long lifespan; minimal maintenance; energy-saving; reduces light pollution. | Higher initial cost; may require specific infrastructure or solar systems. |
| Solar Street Lights | Uses renewable solar energy, minimizing carbon emissions. | Extended operational time of 25,000 hours; energy is stored in batteries for nighttime operation. | Uses renewable energy (solar power); eco-friendly. | Reduces carbon footprint; cost-effective in the long term; reduces reliance on grid power. | Dependent on weather conditions; higher initial investment compared to traditional lighting. |
| Induction Street Lights | Operates with electromagnetic induction, high efficiency. | Long lifespan, but efficiency is lower than LEDs and solar lights. | Less environmental impact compared to traditional lighting but still uses electrical power. | Longer lifespan than halogen and incandescent; no electrodes to wear out. | Higher initial cost; not as popular as LEDs or solar lights. |
| Smart Street Lights | Highly efficient with adaptive lighting using sensors and IoT technology to adjust brightness. | Adjustable brightness based on traffic, time of day, or environmental conditions; real-time monitoring. | Optimizes energy usage; reduces waste; helps monitor traffic and environmental conditions. | Efficient energy use; reduces carbon emissions; adaptive lighting based on real-time data. | High initial setup cost; requires ongoing system management and data collection infrastructure. |
| Incandescent Street Lights | Low efficiency; most energy is wasted as heat. | Low lm/W, lifespan of 1,000 to 2,000 hours. | Generates significant heat, leading to higher energy consumption and increased carbon emissions. | Simple and inexpensive to produce. | Low efficiency; high power consumption; frequent replacements required. |
| Halogen Street Lights | Slightly more efficient than incandescent, but still high heat generation. | Higher lm/W than incandescent, lifespan of 2,000 to 4,000 hours. | Similar environmental impact to incandescent lighting; high energy use. | Longer lifespan and better performance than incandescent. | Still generates excessive heat; higher energy consumption; not suitable for modern applications. |
| Fluorescent Street Lights | Higher efficiency than incandescent and halogen; uses ballasts. | Higher lm/W ratio, lifespan of 8,000 to 10,000 hours. | More energy-efficient than incandescent and halogen; still relies on non-renewable energy. | Better performance than incandescent and halogen; longer lifespan; higher efficiency. | Requires ballasts which increase complexity and cost; still dependent on non-renewable energy. |
| High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lights | High efficiency with long lifespan, often used for urban and highway illumination. | High lm/W ratings, lifespan of 10,000 to 24,000 hours. | Good energy efficiency but still relies on non-renewable energy. | Excellent for large-scale applications; long lifespan; cost-effective in the long run. | Yellowish light reduces color discrimination; mercury content in broken bulbs poses environmental and health risks. |
| Mercury Vapor Street Lights | Less efficient than HPS; previously popular for their lifespan. | Low efficiency, lifespan shorter than HPS; produces bluish-white light. | Toxic mercury content makes them hazardous; not as efficient as modern alternatives. | Longer lifespan than incandescent and halogen; once popular for efficiency. | Contains toxic mercury; low efficiency; largely replaced by better alternatives. |
1. Energy Efficiency The evaluation of street lights heavily depends on their energy efficiency performance. Traditional incandescent and halogen lights waste most of their electrical energy by converting only a small portion into visible light while the rest turns into heat. Fluorescent lights reach higher levels of energy conversion rates when producing visible light output. Urbane settings tend to use HPS lights since their energy efficiency performance makes them a preferred option. The energy efficiency revolution is led by LEDs and solar street lights because LEDs transform 70% of their energy into visible light and solar lights use renewable energy to cut their carbon emissions..
2. Performance Metrics
The evaluation of various street lighting solutions depends on the performance indicators lm/W measurement and lifetime duration and light output. The performance of incandescent lights includes a low lm/W rating combined with a short lifespan that reaches between 1,000 to 2,000 hours. The performance of halogen lights includes a lm/W rating between 2,000 to 4,000 hours and a corresponding lifespan. Fluorescent lights deliver superior lm/W performance and operate for 8,000 to 10,000 hours. The lifespan of HPS lights reaches between 10,000 to 24,000 hours while maintaining a high lm/W rating. LEDs outperform other lighting technologies because they reach a maximum lm/W rating of 100 and operate for 25,000 to 50,000 hours or longer. Solar street lights provide extended operational time of 25,000 hours while delivering renewable power generation as their main advantage.
3. Lifespan and Maintenance Street light durability shows wide variation because it determines both maintenance expenses and asset worth. Maintenance expenses rise because traditional incandescent and halogen lights need regular replacement. The extended operational life of fluorescent and HPS lights reduces the number of required replacements. The extended operational lifetime of LEDs and solar street lights reaches 50,000 hours or beyond which makes them an economical lighting solution for extended periods. Smart street lights improve maintenance efficiency through their ability to monitor systems remotely and adjust lighting automatically.
4. Environmental Impact Street light implementation requires thorough evaluation of their environmental effects. Traditional incandescent and halogen lights utilize excessive energy while generating significant heat which enhances carbon emission levels. The energy-efficient fluorescent and HPS lighting systems use non-renewable power sources. LEDs together with solar street lights represent the future of environmental sustainability because LEDs minimize energy usage and solar lights operate using renewable power. The adaptive lighting features together with real-time monitoring systems in smart street lights optimize energy efficiency and minimize waste by ensuring sustainable operation.
Applications and Usage Scenarios of Street Lights
Street lights are utilized in diverse settings, each requiring specific lighting solutions.
Urban vs. Rural Settings
Cities often have high concentrations of people and vehicles during the day, requiring street lights to have a higher intensity. During the night, LEDs and HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) lights which are bright and easy to maintain are used in urban centers. On the other hand, rural regions tend to have lower traffic and have different safety demands; hence, they utilize simpler lighting systems during the night. When designing street lights for urban and rural areas, light intensity, coverage, energy consumption, and other factors must be taken into account.
Specialized Lighting Needs
Highways and parks demand street lights that provide extensive coverage and high visibility to ensure driver safety at high speeds. Soft ambient light with sufficient security can be used in parks and recreational areas. These special requirements have to be known in order to select the most suitable design of street lights, ensuring practicality without sacrificing aesthetics. Additionally, light source options are crucial when considering parking lot, public street lighting, and outdoor spaces, as they need specific lighting designs that deliver optimal light distribution to meet safety, security, and visibility demands.
Environmental and Economic Factors of Street Lights
The choice of street lights significantly impacts both the environment and the economy. Evaluating these factors is essential for making informed decisions.
Environmental Impact
The older street lighting technologies of halogen and HPS use greater energy while releasing higher amounts of carbon dioxide than LED and solar street lights. Solar lights together with LEDs lead to increased environmental friendliness because they decrease energy use while lowering carbon footprints which helps sustainability advancement. The selection process of street lights requires careful evaluation of environmental impact because communities actively work to decrease their ecological impact.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
To start with conventional street lights, they may cost less than modern designs for LED and solar street lights, but their operational expenses resulting from higher consumption of energy are very costly as these traditional lights consume more energy than should be needed and their lifespan is also shorter. LED and solar street lights, which have higher initial expenses, however, allow for greater savings on energy bills over time and require very minimal maintenance. This makes them a cost-effective choice in the long run, providing a favorable return on investment for municipalities and homeowners alike.
The Rise of Solar Street Lights: A Game Changer
Solar street lights represent a breakthrough innovation in street lighting because they provide superior advantages compared to conventional systems.
Advantages of Solar Street Lights
Solar street lights use renewable solar power to replace traditional non-renewable energy sources thus producing fewer carbon emissions. Solar-powered lighting systems provide optimal illumination while using low power consumption through LED technology. The installation and maintenance of solar lights prove simpler than traditional options because they function well in areas without power grid accessibility. Solar street lights offer communities an effective combination of sustainability and power efficiency which attracts them as a lighting solution.
Inlux Solar: Leading the Way in Solar Street Light Solutions
Inlux Solar is one of the top manufacturers of the solar street light category. Because of the well-defined commitment to innovation, quality, and customer service, Inlux Solar is a brand people trust. Inlux Solar mitigates challenges like energy consumption and maintenance costs tied to traditional street lights by providing efficient, durable, and sustainable solutions with long life and less maintenance. Regardless of the type of street light, Inlux Solar ensures that each product delivers optimal performance. Monuments of the company’s progress are products that incorporate advanced technology while caring for the environment, which makes them the ideal choice for every street lighting need, offering bright light, and cost-effective solutions with a lower initial investment.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The best thing about streetlights is that there are super different types of them. Such types get the advantages of both modern and older technology, like halogen, fluorescent, LED, and even solar lights. As technology develops and expands, brands like Inlux Solar have the best potential to lead the industry in street light sustainability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Selecting suitable street lights needs extensive evaluation of the anticipated energy usage, eco-friendliness, and even the overall budget. The proper street light design usage can foster security, lower costs, and make the world a cleaner place. Inlux Solar is a fantastic design option to cater to such lighting needs.