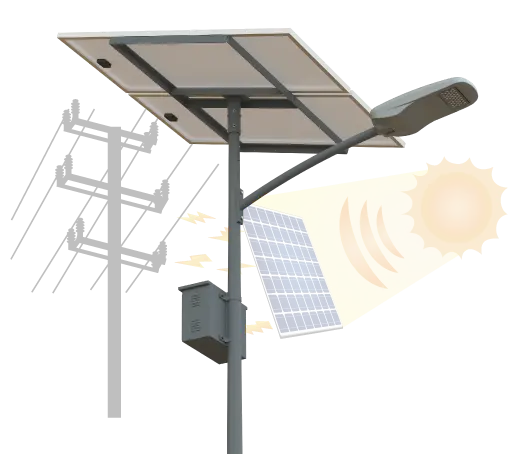
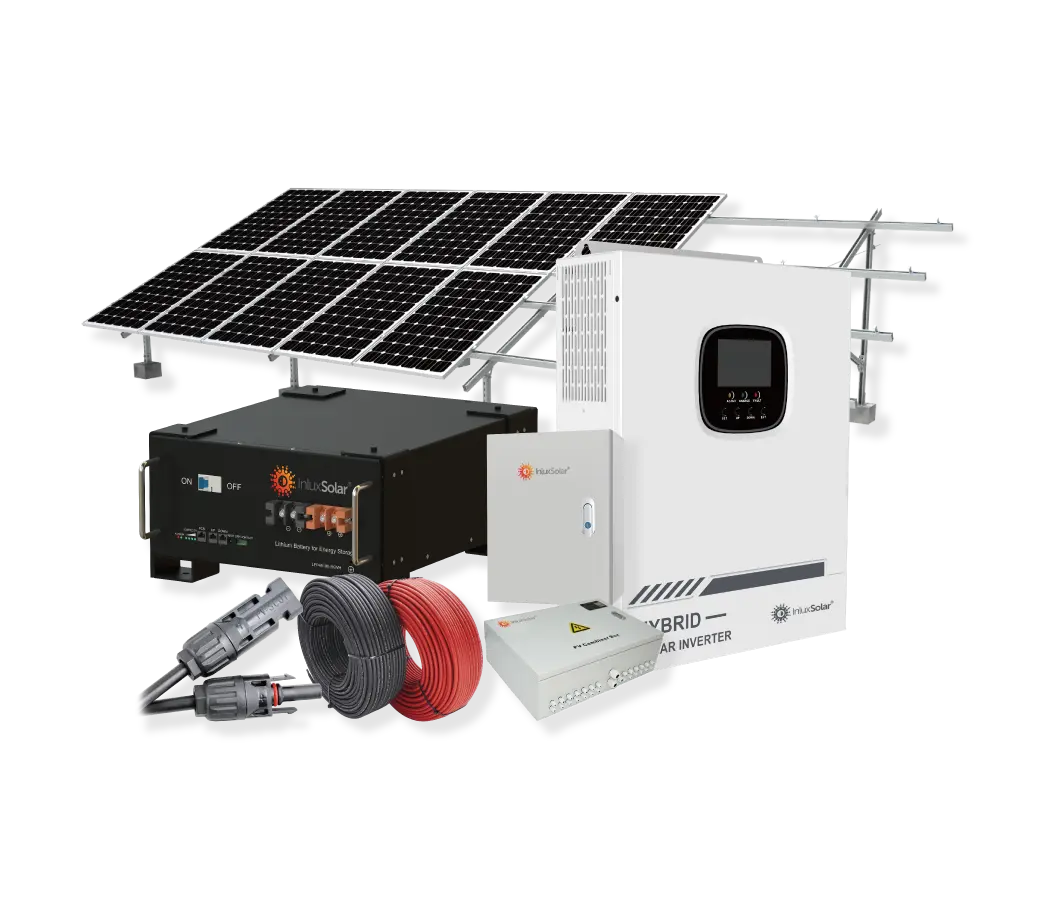
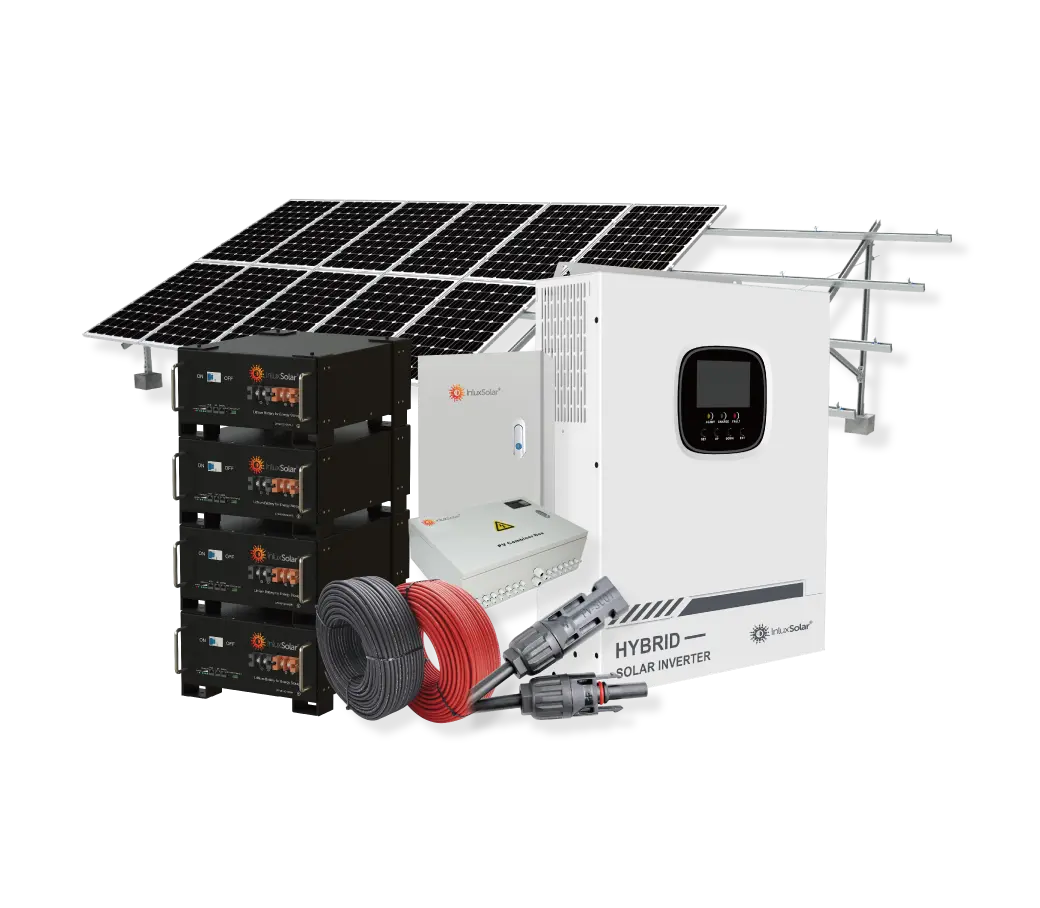
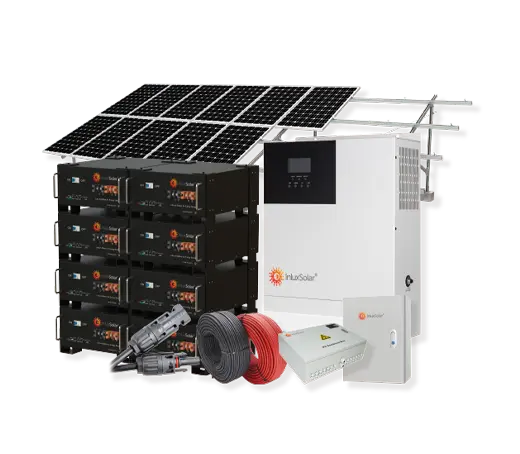
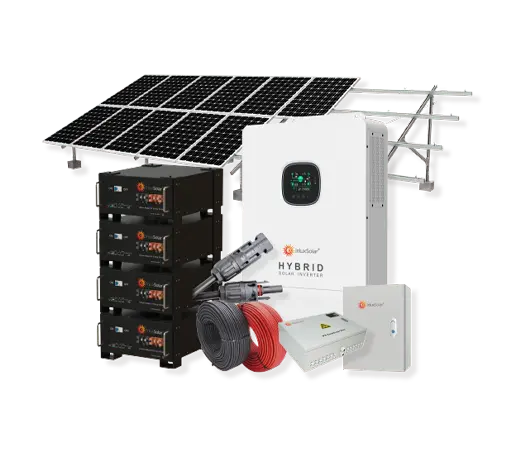
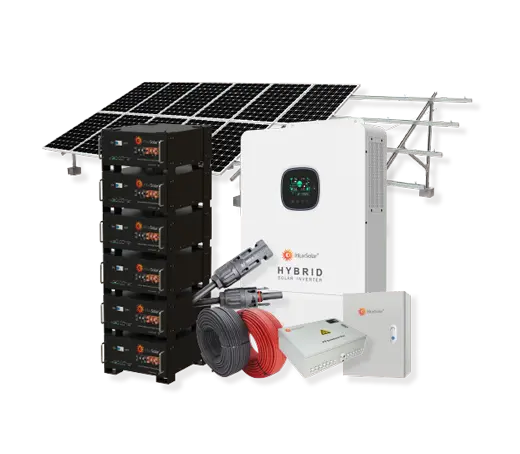
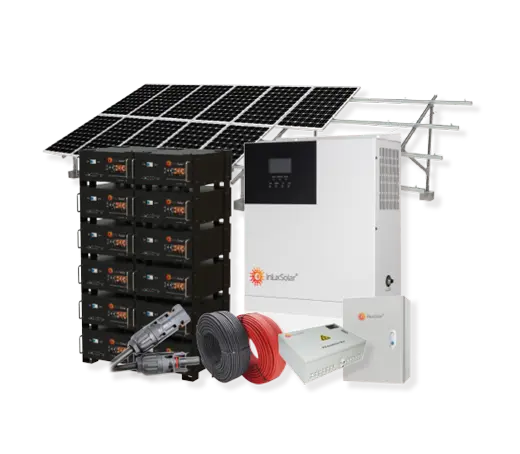
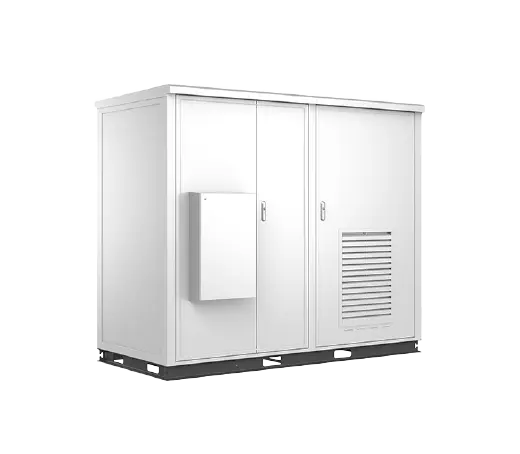
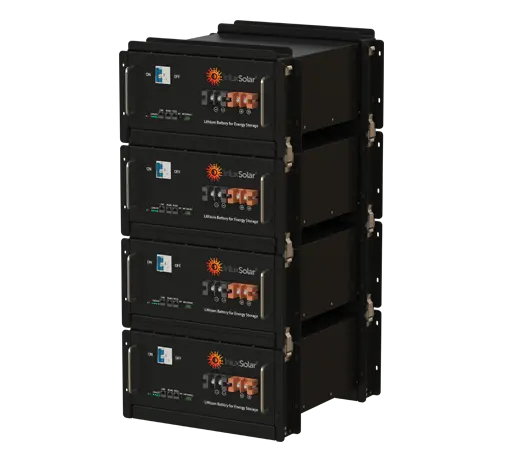
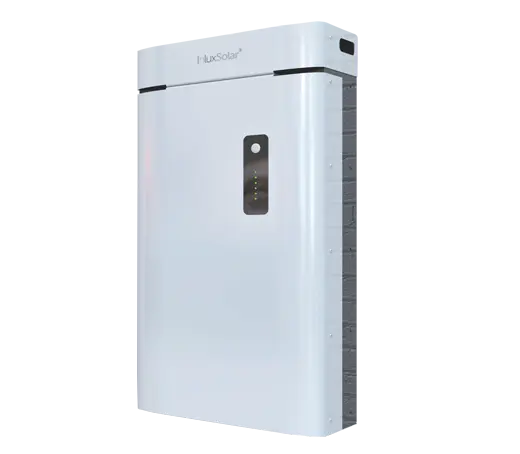
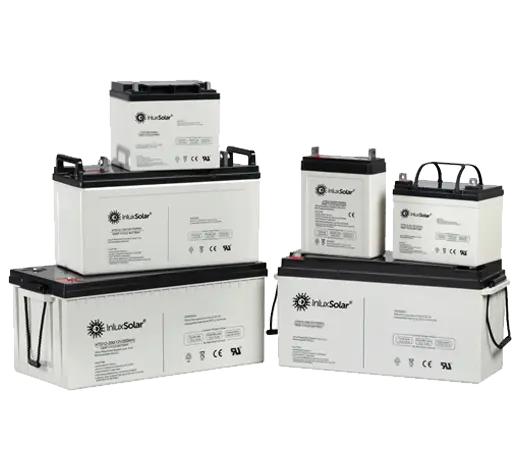
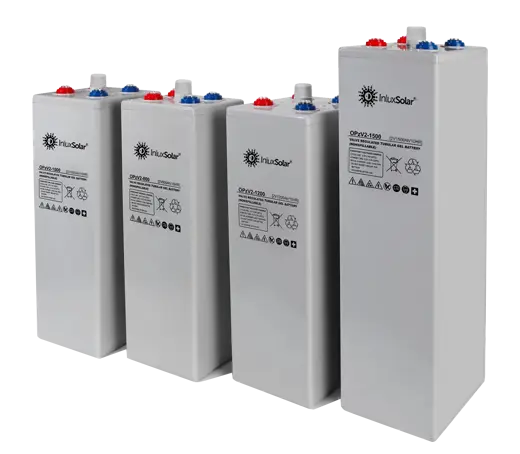
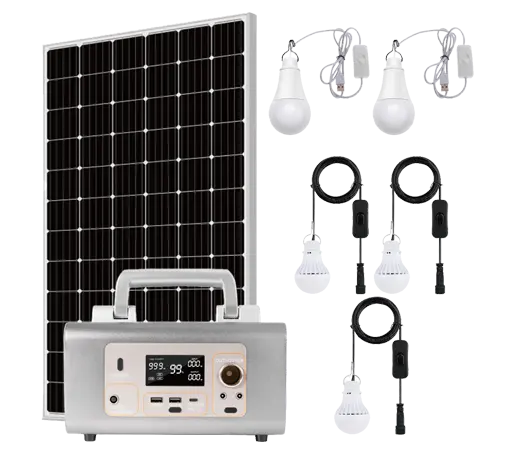
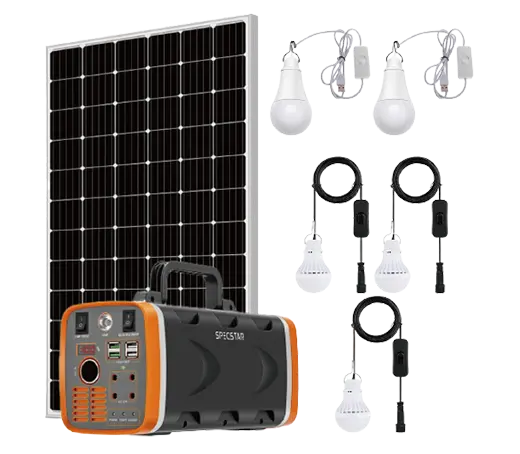
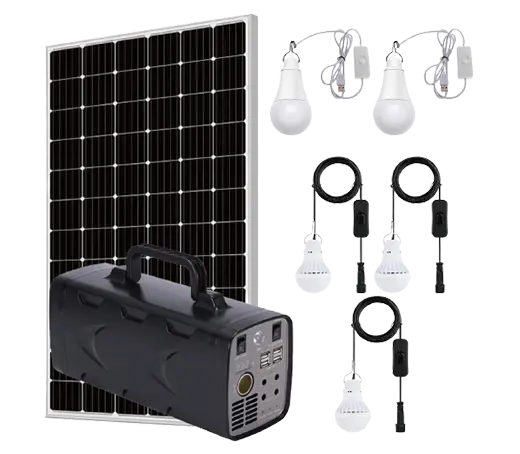
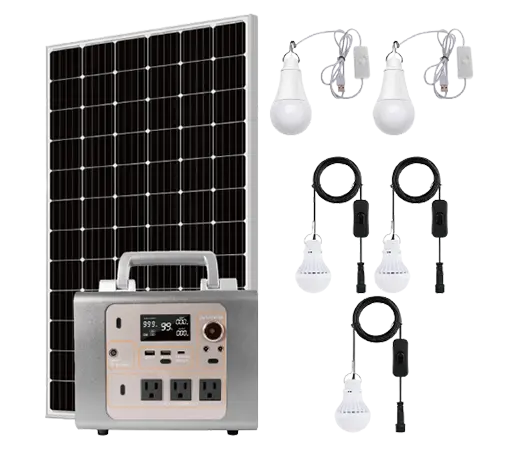
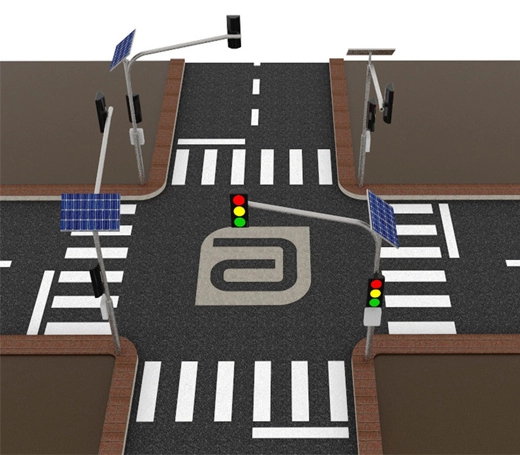
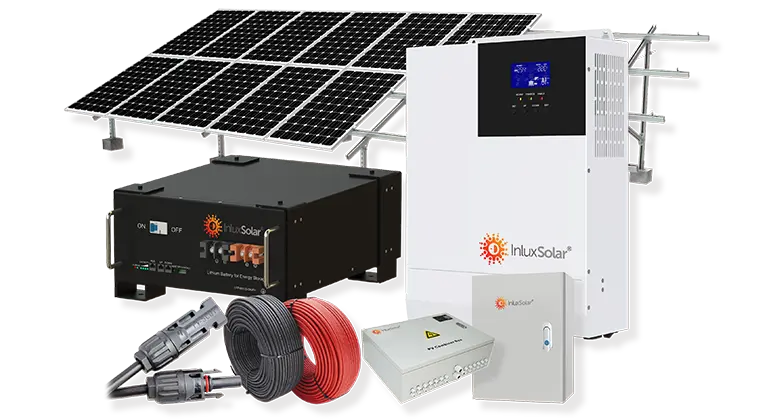
Solar power systems harness energy from the sun, which is an abundant and renewable source of energy. As long as the sun continues to shine, solar power will be available.


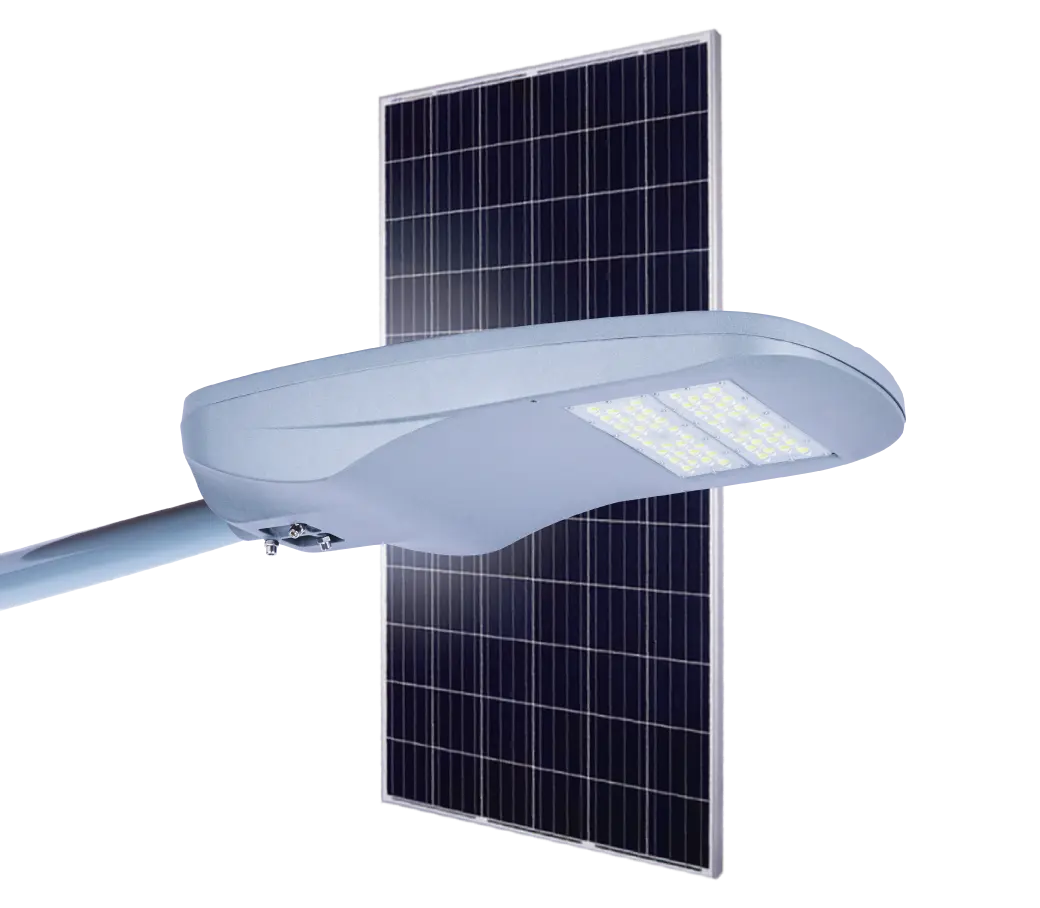
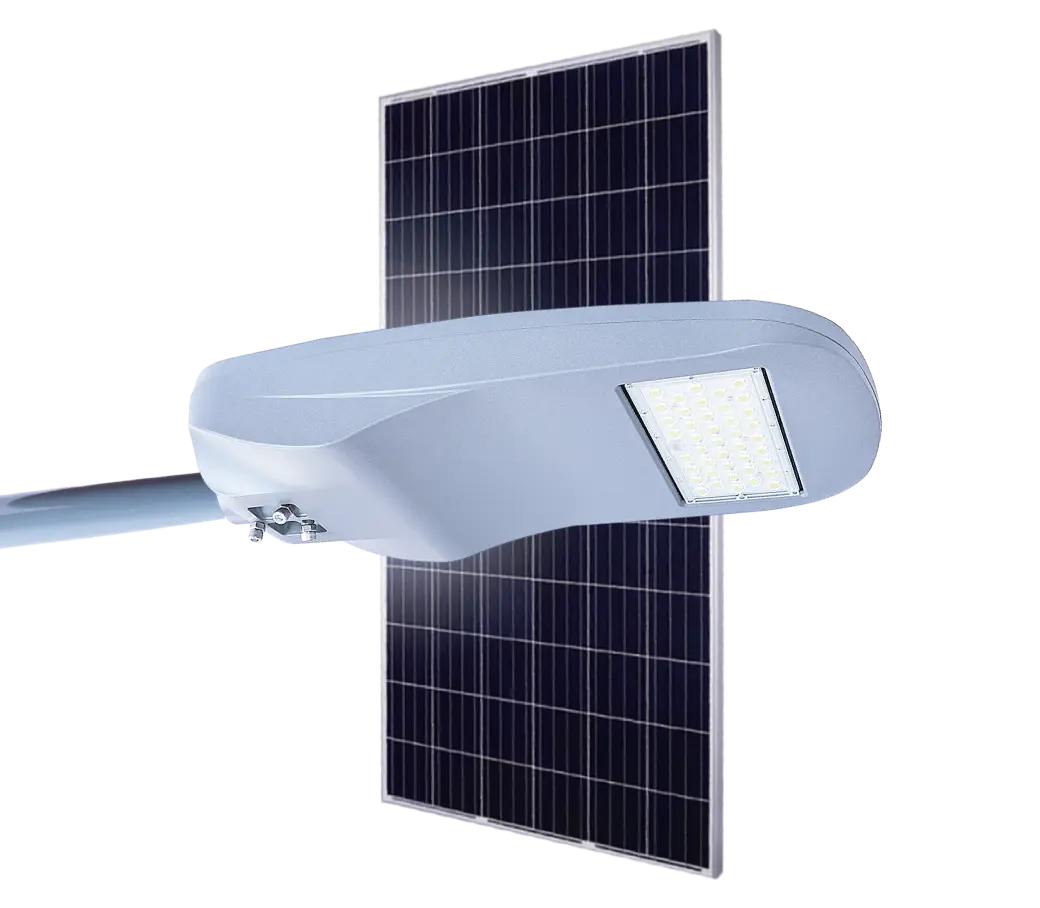
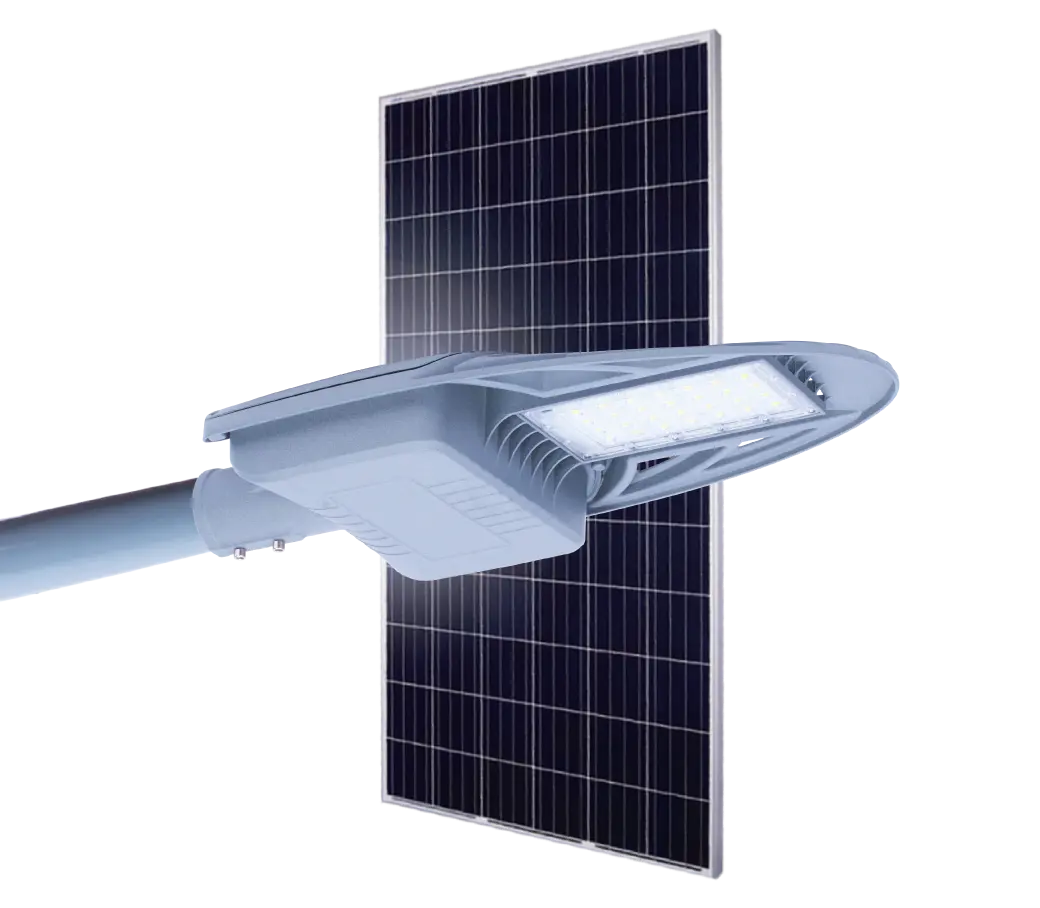
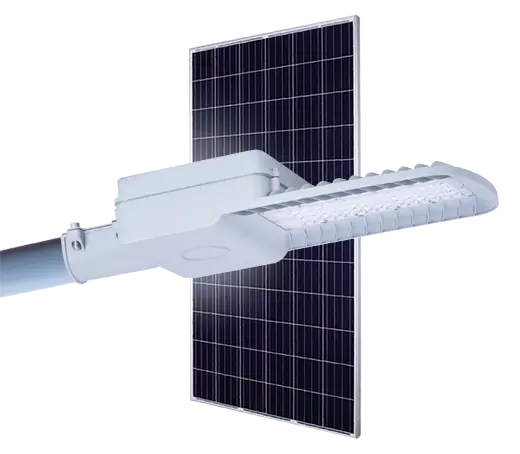
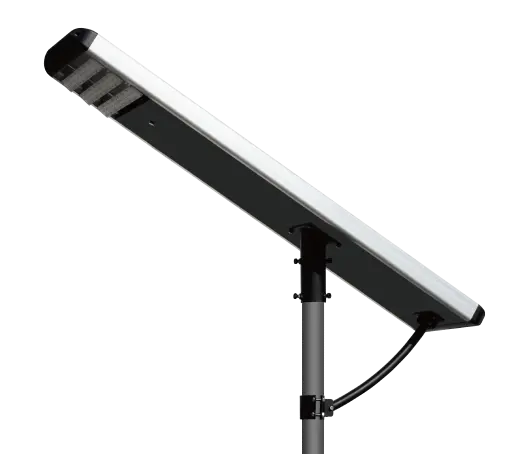
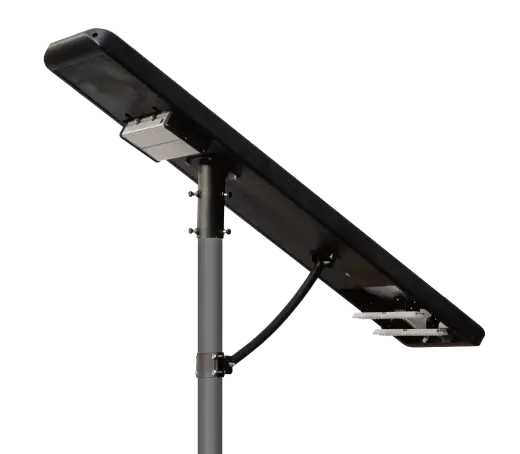
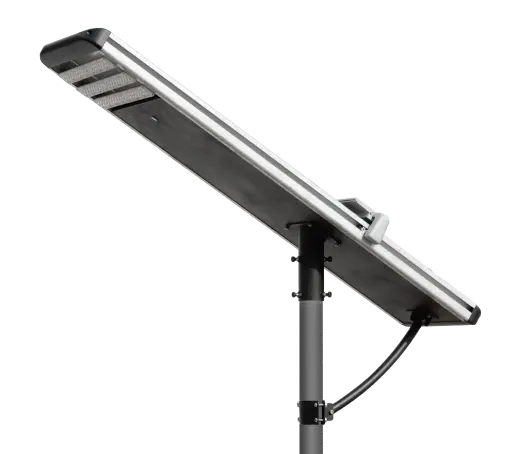
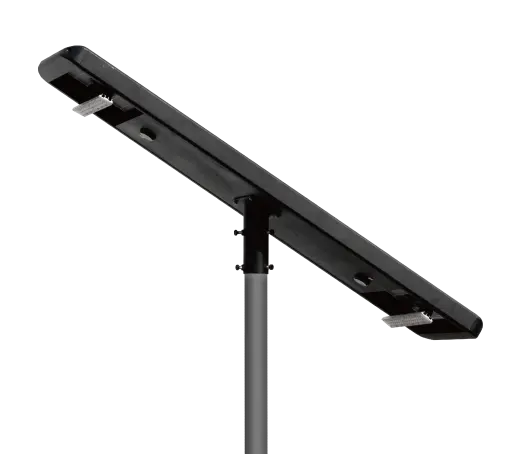
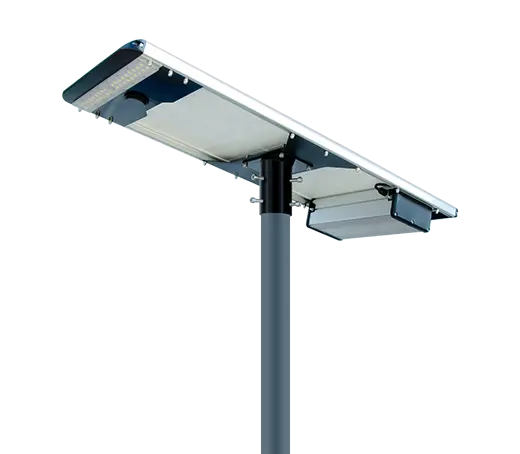
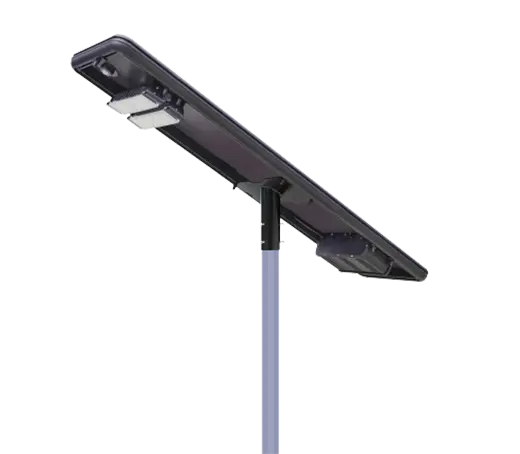
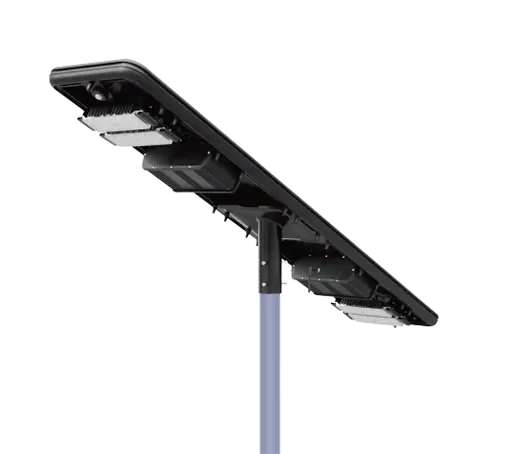
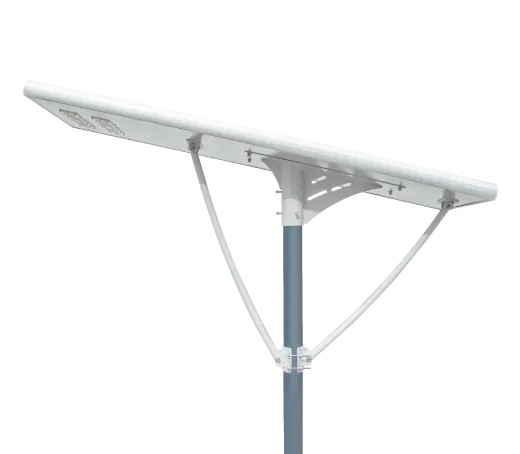
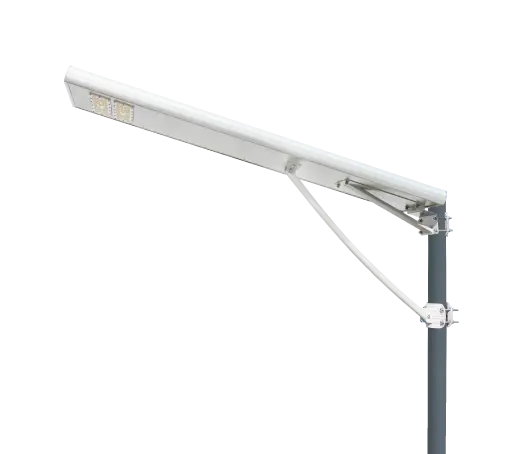
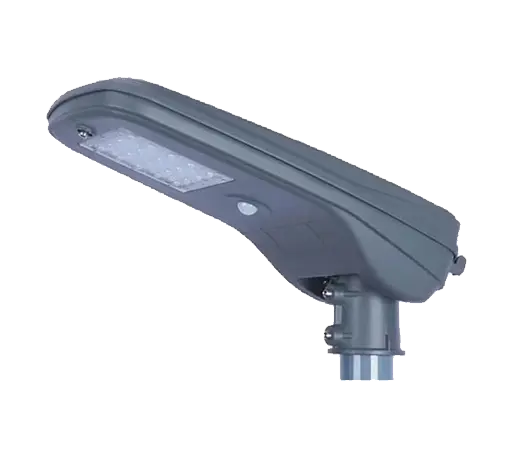
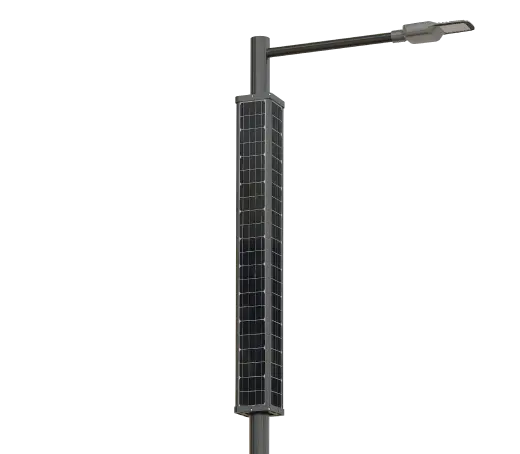
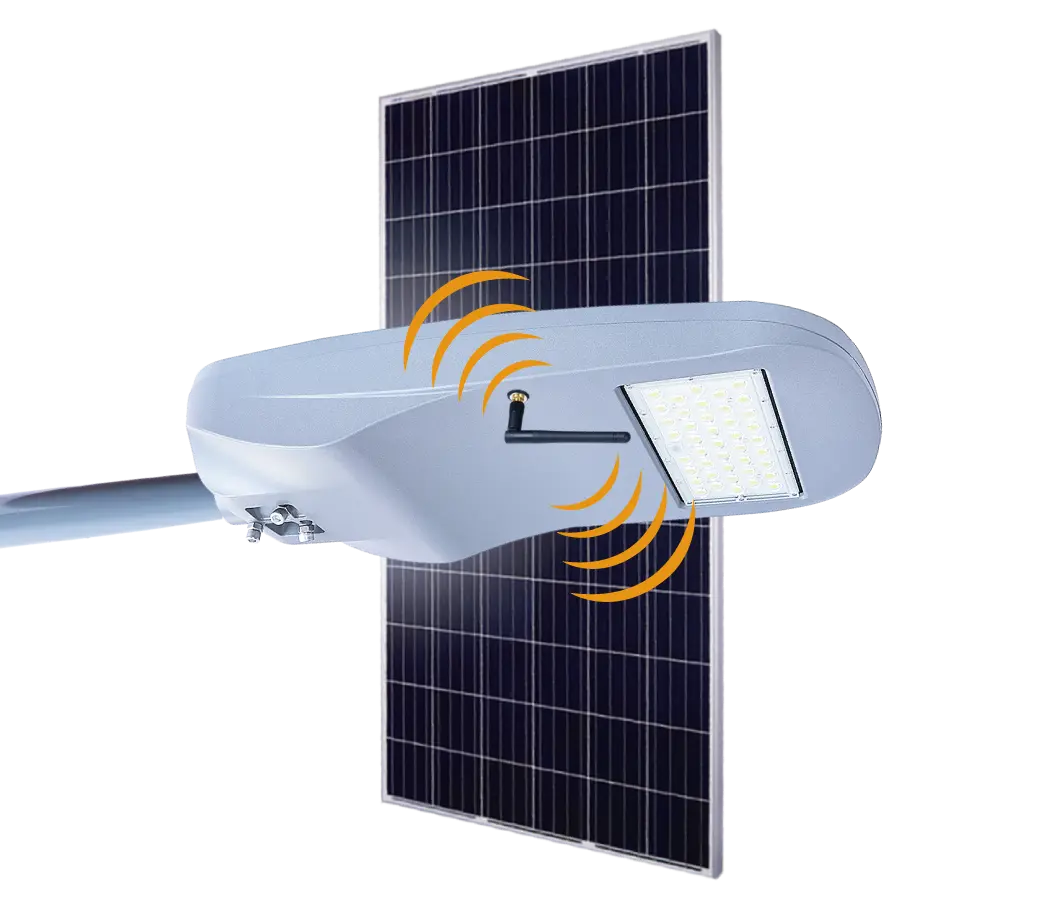
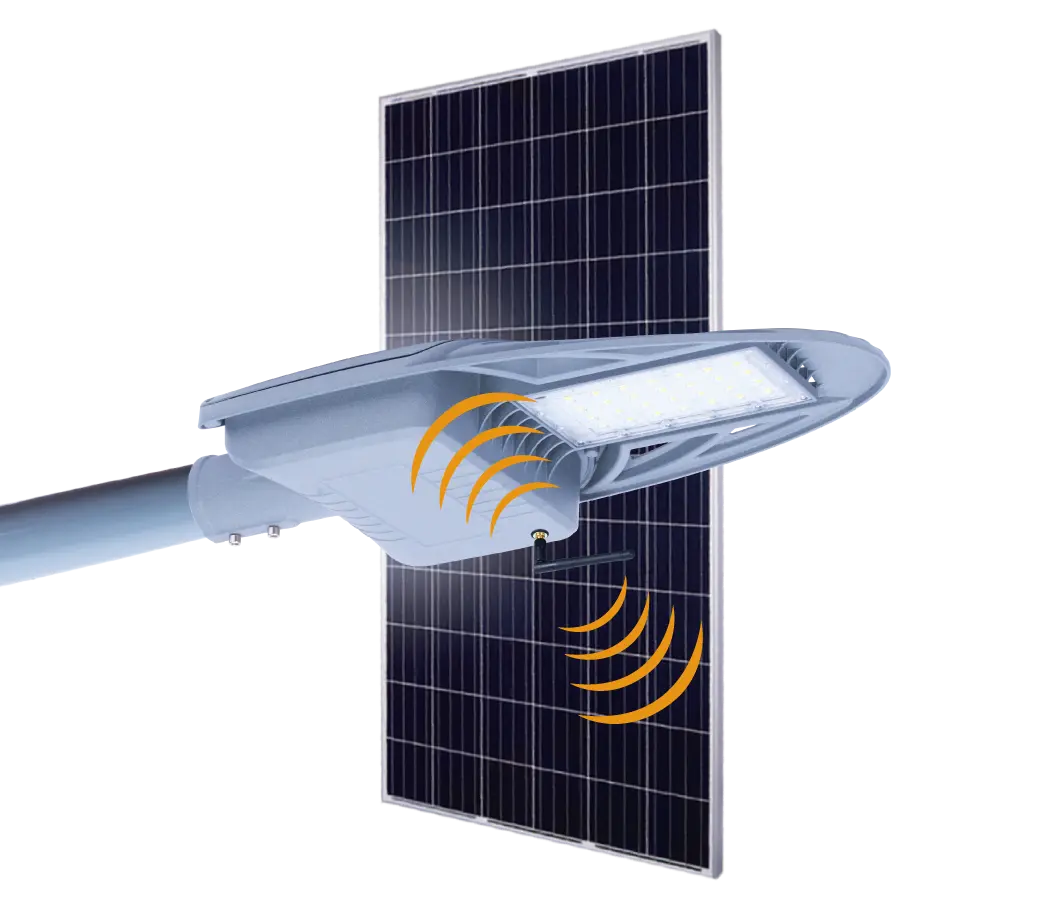
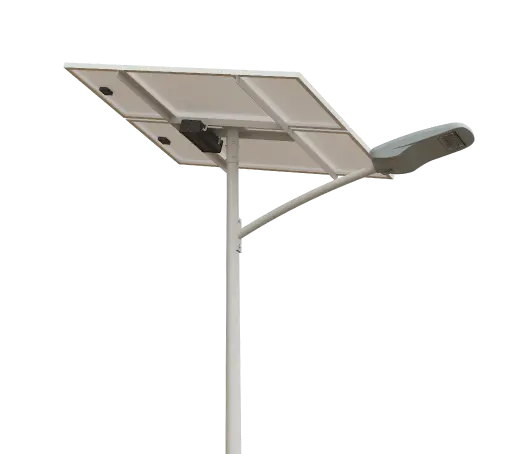
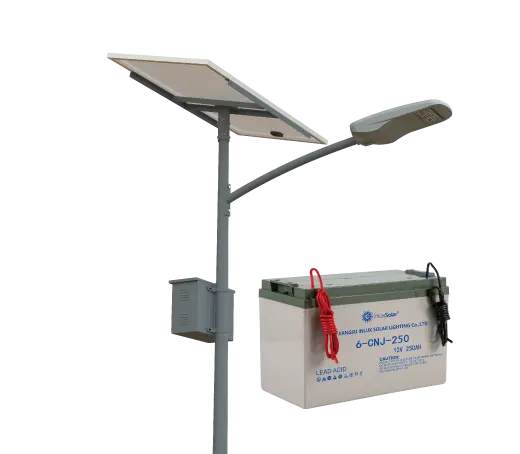
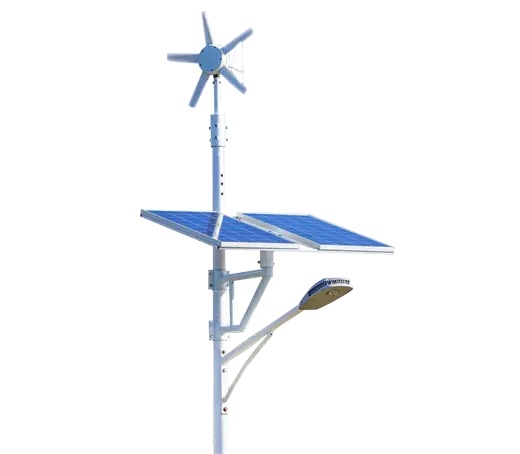
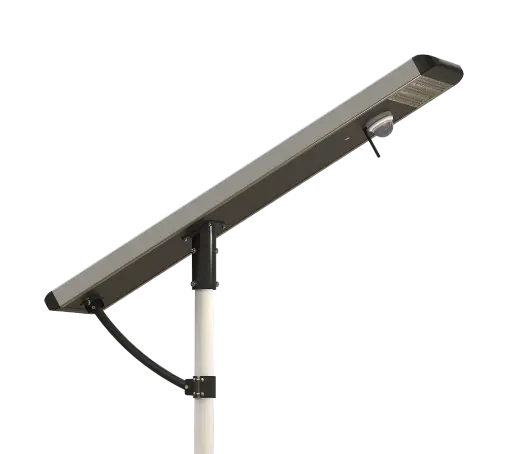
- Solar Street Light
-
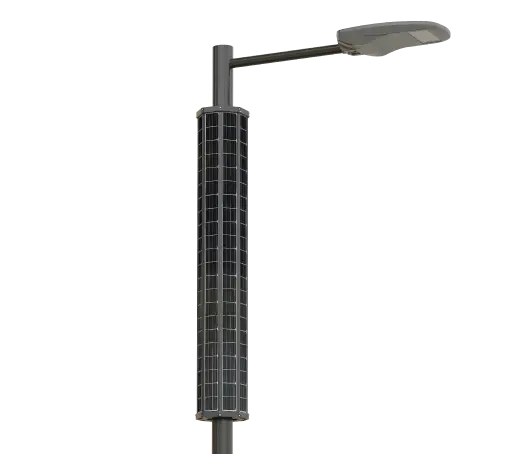
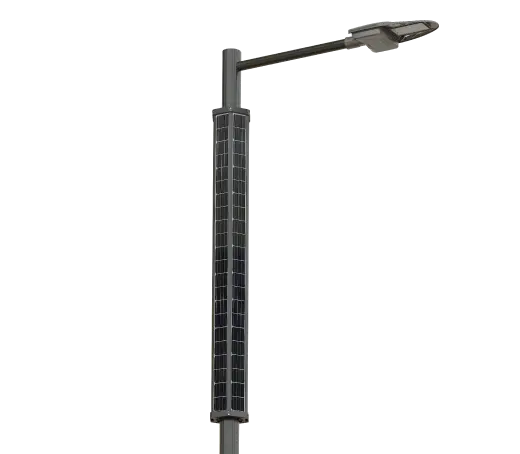
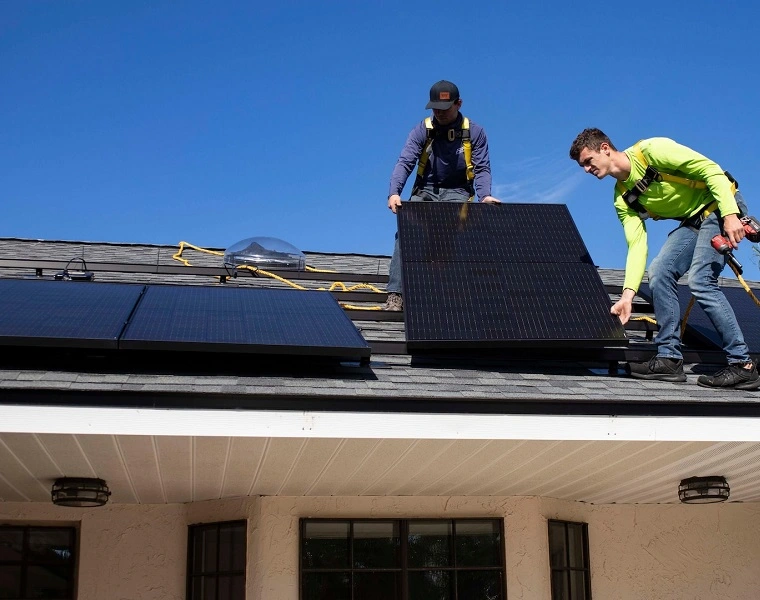
Solar Power System
-
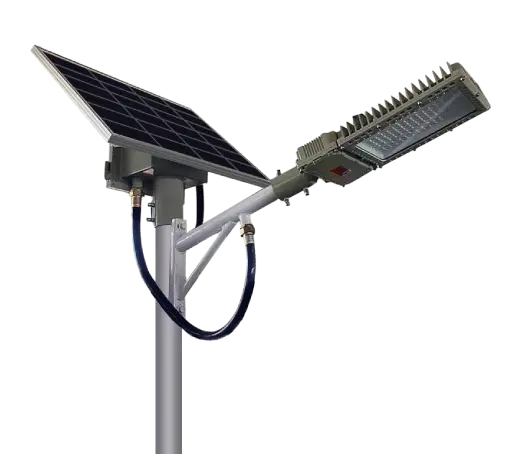
Commercial LED Outdoor Light
-
Solutions
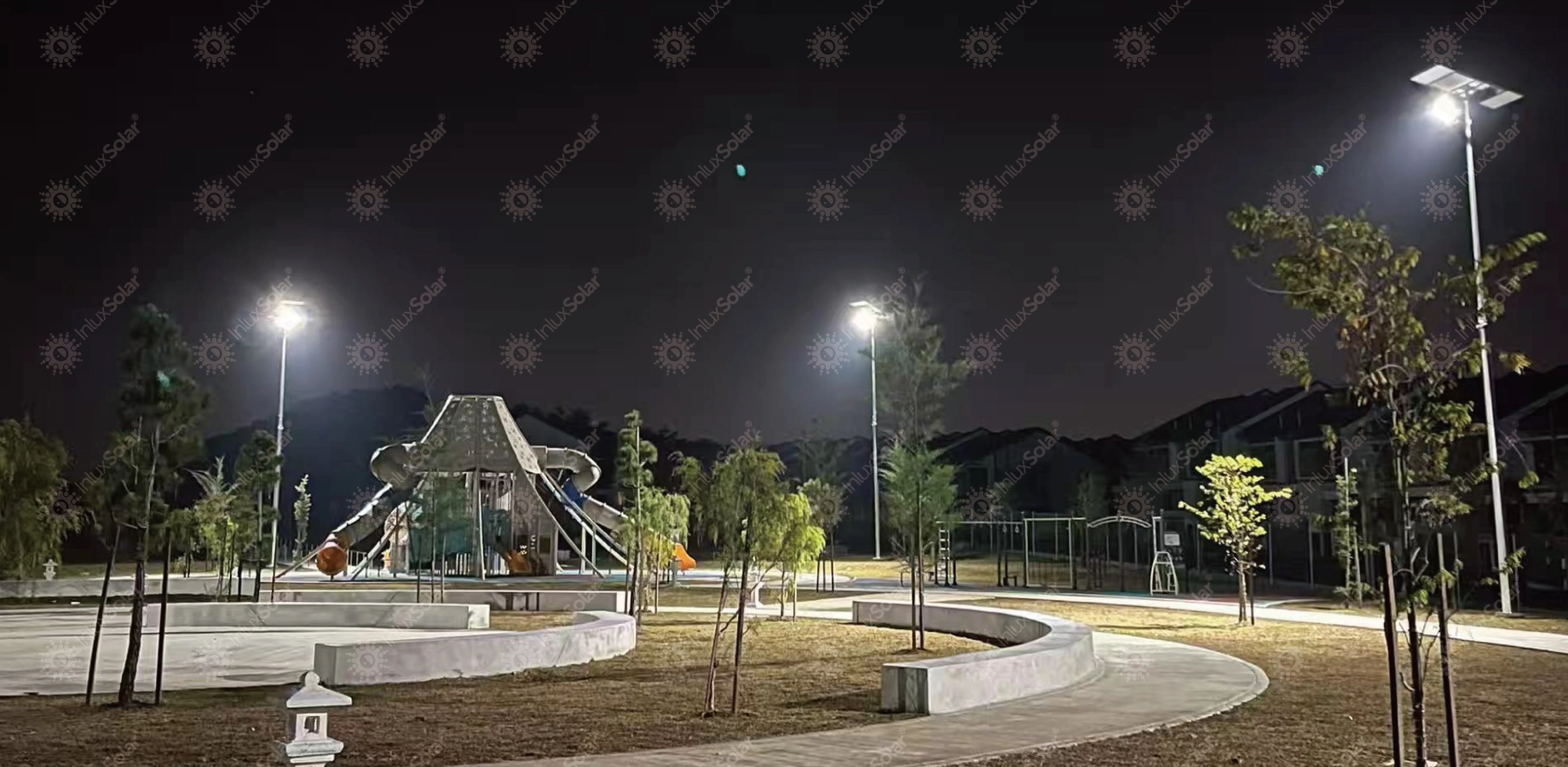
 SolutionsInlux Solar Street Lights are designed to provide energy-efficient lighting solutions for a wide range of applications. They are particularly suitable for use in rural areas, highways, city streets, public parks, sidewalks, parking lots, and commercial properties.
SolutionsInlux Solar Street Lights are designed to provide energy-efficient lighting solutions for a wide range of applications. They are particularly suitable for use in rural areas, highways, city streets, public parks, sidewalks, parking lots, and commercial properties. -
Projects
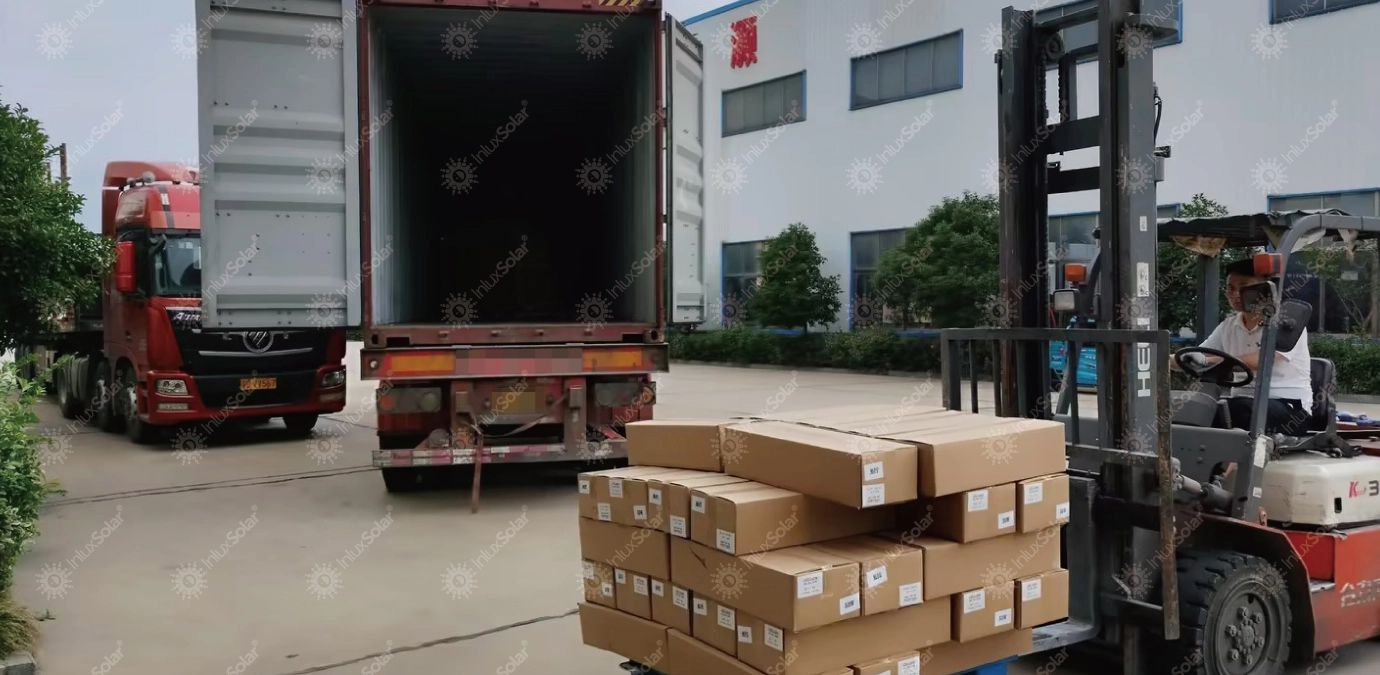
 Projects1000+ Projects in 100+ Countries
Projects1000+ Projects in 100+ Countries -
About Us
 About UsAs a Leading international manufacturing company, INLUX SOLAR develops and manufactures advanced solar outdoor lighting and power system solutions for the worldwide commercial & municipal projects.
About UsAs a Leading international manufacturing company, INLUX SOLAR develops and manufactures advanced solar outdoor lighting and power system solutions for the worldwide commercial & municipal projects. - Expertise
- Contact Us
-
×
 English
English français
français Español
Español