Introduction
The primary function of traffic signals in modern cities revolves around their fundamental role in managing vehicles and pedestrians through designated color sequences. The dimensions of traffic lights differ according to their intended use and installation position. Standard vehicle signals feature 8 or 12 inches diameter lenses per signal while pedestrian signals maintain a smaller size. Factors such as visibility, traffic speed, and roadway design influence these dimensions. Traffic safety and control operations in communities require thorough planning because traffic light size specifications vary for different purposes.
The Standard Dimensions of Common Vehicle Traffic Lights
The most common type of traffic signal is the standard vehicle signal which is formed with three lenses colored red, yellow and green that may be arranged vertically or horizontally. Although there are slight differences between regions and manufacturers, there tend to be accepted standard measurements for these important devices. For example, in North America, it is common practice to use 12 inch diameter lenses for each signal head in which case horizontally mounted three-light signals would have a width of about 36 inches while the vertically mounted signals would be around 36 to 40 inches tall, all of which is estimated without taking the mounting hardware or backplates into consideration.
The standard lens diameter for these signals in Europe and some other parts of Asia is normally 200 or 300 millimeters which means the signal housing box would have wide varying dimensions. In the case of three-light assemblies with 300mm lenses, the width of a horizontal arrangement would be about 900mm and the height of the vertical arrangement would be the same. The specified values are not random, but made with the intention to provide the maximum amount of sight for drivers coming towards an intersected road so they are able to notice the signal changes and react in a timely manner.
| Region | Lens Diameter (inches/mm) | Typical Width (3-Light Horizontal) | Typical Height (3-Light Vertical) |
| North America | 12 inches | ~36 inches | ~36-40 inches |
| Europe/Asia | 200 mm (~8 inches) | 600 mm (23.6 inches) | 600-700 mm (23.6-27.6 inches) |
| Europe/Asia | 300 mm (~12 inches) | 900 mm (35.4 inches) | 900-1000 mm (35.4-39.4 inches) |
Typical Diameter and Arrangement of Signal Heads
Each signal head unit which contains red yellow and green lenses maintains uniform diameter dimensions in its specific assembly configuration. The standard diameter for vehicle signals stands at 12 inches (300mm). Local regulations together with intersection geometry determine how these signal heads should be arranged either vertically or horizontally. The placement of signal lights as vertical or horizontal arrangements depends on snow conditions and local regulations that consider both snow accumulation and aesthetic standards and vertical clearance requirements.
Overall Height and Width of Standard Units
The overall height and width of a standard traffic light unit encompass not only the signal heads but also the surrounding housing and any necessary mounting brackets. The dimensions play an essential role in achieving correct intersection placement and visibility. The traffic light assembly dimensions depend on the number of lanes and pedestrian crossings and the requirement for additional signage. Safety optimization and traffic flow optimization occur through thorough evaluation of these factors during design and installation construction periods.
Exploring the Varied Sizes of Specialized Traffic Signals
In addition to the common vehicle signals, there exists a variety of specialized traffic lights, each with their own defined scope, functions, and dimensions. Pedestrian crossing signals, for example, are generally smaller in size than vehicle signals. Their lenses, which are marked with a “walking person” and a “hand” symbol, have diameter measurements ranging from 8 to 9 inches. This smaller dimension is adequate for pedestrian recognition while assisting to separate them from the larger vehicle signals. The traffic signal design for pedestrians ensures that their signals are noticeable without overwhelming the standard vehicle signals.
Arrow signals, which permit turning movements like left or right turns, also come in lens diameter sizes. Standard traffic signals typically utilize 12-inch lenses, while others, especially those for protected left or right turns, often utilize smaller lenses, usually 8 inches in diameter. These arrow signals also need to be large enough to be seen by drivers easily while not too wide to cover the main vehicle signal indications. Other newer signals that are on the rise in urban environments are bicycle signals, which often come with smaller lenses, in reference to the visual field of cyclists, usually at 8 inches. Bus lane signals that control traffic in reserved bus lanes may also have specific measures as defined by the local authority with relation to the design of the highway.
| Signal Type | Typical Lens Diameter (inches) | Typical Dimensions (varies) |
| Pedestrian Signal | 8-9 inches | Smaller, single or dual head |
| Arrow Signal | 8-12 inches | Single head, various shapes |
| Bicycle Signal | 8 inches | Smaller, often single head |
| Bus Lane Signal | Varies | Can be similar to vehicles or smaller |
Dimensions of Pedestrian Crossing Signals and Push Buttons
Pedestrian crossing signals use design elements that make them highly noticeable to people waiting to cross streets. Pedestrian crossing signals possess dimensions that fall below vehicle signals and their lens diameters measure between 8 to 9 inches. The signals provide both visual countdown timers and touchable indicators which help people with vision impairments. The pedestrian signal activation buttons maintain standardized dimensions and mounting heights for easy accessibility by users.
Size Specifications for Left/Right Turn Arrow Signals
Traffic intersections depend on left and right turn arrow signals to establish protected turning phases for traffic management purposes. The standard arrow signal design features 12-inch lenses but 8-inch lenses are used when main vehicle signals need priority or when space availability is restricted. Arrow signals receive precise attention regarding their size and brightness to guarantee visibility for drivers who plan to turn.
Understanding Bicycle and Bus Lane Signal Dimensions
In tandem with the rising focus on eco-friendly transportation, bicycle and bus lane signals are on the rise within city metropolitan areas. Typically, bicycle signals are smaller than standard vehicle signals and use 8-inch lenses exhibiting a bicycle symbol instead of a circular lens. Such dimensions fit the visual field of a cyclist merge area. Regulations for specific road designs also determine the size of the bus lane signals, they can be compact or resemble standard vehicle signals, and are used to control the traffic in the dedicated bus lanes.
The Impact of Overall Traffic Light Height on Size
The traffic light height must be positioned as per the range of vehicle obstructions such as trees, furniture on streets and other cars, so that there is full visibility from the driver’s seat. Different road settings lead to different styles of construction and designs which in turn determine the height of traffic lights. Depending on the type of signal, whether vehicle or pedestrian, traffic signal height also varies. Urban regions with high traffic and complicated roads usually place the traffic light higher up, allowing for the lights to be fully visible from a distance. Depending on the lanes being used, the signal heads at complex road intersections where there are multiple lanes, can be placed so that the signal is visible in every lane.
This traffic control device is sighted from a lower view compared to vehicle signals for pedestrians. Signals for pedestrians should be placed at the average person’s eye level, approximately 4 to 5 feet above the ground, so that the individual walking can see and make the appropriate response . Furthermore, the height of pedestrian signals might change based on the volume of pedestrian traffic on the street, the configuration of the intersection, and the area around it. Sometimes, signals may be placed on poles or at ground level for easy viewing and reaching by pedestrians, especially those with physical disabilities. There are different standards for the height of signals in different countries and regions depending on the volume of traffic passing, the layout of the region, and local laws regarding safety.
| Region | Signal Type | Typical Height (inches) | Description |
| North America | Standard Vehicle Signal | ~36-48 inches | Mounted higher for better driver visibility, especially at busy intersections. |
| Europe/Asia | Standard Vehicle Signal | 1500-1800 mm (59.1-70.9 inches) | Typically mounted on taller poles for better visibility on multi-lane roads. |
| North America | Pedestrian Signal | ~48-60 inches | Mounted at eye level for pedestrians, making it easily visible for walkers. |
| Europe/Asia | Pedestrian Signal | 1200-1500 mm (47.2-59.1 inches) | Often installed lower than vehicle signals for pedestrian convenience. |
| All Regions | Arrow Signal | ~36-48 inches | Arrow signals for turning lanes are mounted at a similar height to vehicle signals, but may be lower in some cases. |
| All Regions | Bicycle Signal | ~36-48 inches | Typically mounted at cyclist’s eye level, either near or below vehicle signals. |
Key Factors Influencing the Overall Size of Traffic Light Assemblies
The complete dimensions of a traffic signal set are not only defined by each signal head’s size. There are some basic elements which determine the size and shape of these essential devices used to control traffic. One important element is the primary dimension of the highway which includes its width and the number of lanes. Wider and multi-lane intersections tend to use more sophisticated and larger traffic signal assemblies to provide reasonable sight for all drivers coming from different directions. The range at which drivers need to see the signals clearly also matters. Increased speeds and greater distances require bigger lenses and possibly bigger assemblies.
As for the other aspects, the complexity of the intersection and traffic volume also plays a significant role. Considerations of additional signal heads, such as protected left-turn arrows, is relevant in complex intersections, as these approaches tend to have greater traffic volumes. In addition, larger traffic control systems like integration of pedestrian Active Signal, countdown timers, and other regulatory or warning signs also increase the overall spatial requirements of the traffic light assembly. There are local rules and standards given by the local transportation authorities which also control the dimensions of the traffic light with its position on the mast.
| Factor | Impact on Size |
| Roadway Width & Lanes | Wider roads often require larger assemblies |
| Driver Visibility | Longer sight distances necessitate larger lenses |
| Traffic Volume & Complexity | More complex intersections may need more signal heads |
| Integration of Other Devices | Inclusion of pedestrian signals, signs increases size |
| Local Regulations | Specific standards dictate size requirements |
The Impact of Roadway Width and Lane Configuration
The spatial arrangement of an intersection, especially its road’s width and lane count, influences the signal arrangement and its coverage area. Larger roadways require signal assembly with greater dimensions so that the signals can be seen from all lanes. Multi-lane intersections may also require additional signal heads for specific lanes to provide clear indications to drivers in different parts of the intersection. The signals are placed as strategically as possible to ensure maximum clarity and the least amount of confusion possible for drivers.
Considering Driver Visibility and Safety Regulations
A driver’s observation is taken into account while designing the position of traffic lights. Safety laws state that a traffic light must be within a certain distance to be viewed to allow adequate reaction time to the signal changes, thus helping prevent collision. This requirement often sets the altitude, position, and dimension of the signal lens and the traffic light assembly. Additionally, the light conditions, ambient obstructions, and the approach speeds of vehicles are factors which may affect safety, flow of traffic, and response time, so they are all considered.
Global Standards and Regional Differences in Traffic Light Dimensions
Traffic regulations between nations differ thus creating obstacles for traffic light implementations. The variations stem from disparate areas’ customary ways that combine traditional customs with historical practices and engineering principles. Vehicle signals in North America typically use 12-inch lenses but European and Asian countries prefer their signals to have 200mm or 300mm lenses.
Worldwide color schemes as well as signaling elements vary between regions. Pedestrian signals with their red-yellow-green sequences maintain a worldwide common understanding so different regions can use distinctive flashing patterns that identify their specific areas. The yellow light functions as a warning to drivers to reduce speed before the red signal appears while the green signal indicates it is safe for vehicles or pedestrians to move forward. The traffic management and smooth signal phase transitions depend on these specific color sequences. The global variation of traffic signals requires traffic planners and engineers to use it as a foundation when establishing international projects and best practices. All traffic standards maintain the essential requirement of delivering clear messages to road users. Traffic signals designed with consideration for yellow light and green signal help control and optimize traffic movement for safety purposes.
Inlux: Providing Robust Infrastructure for Reliable Traffic Management
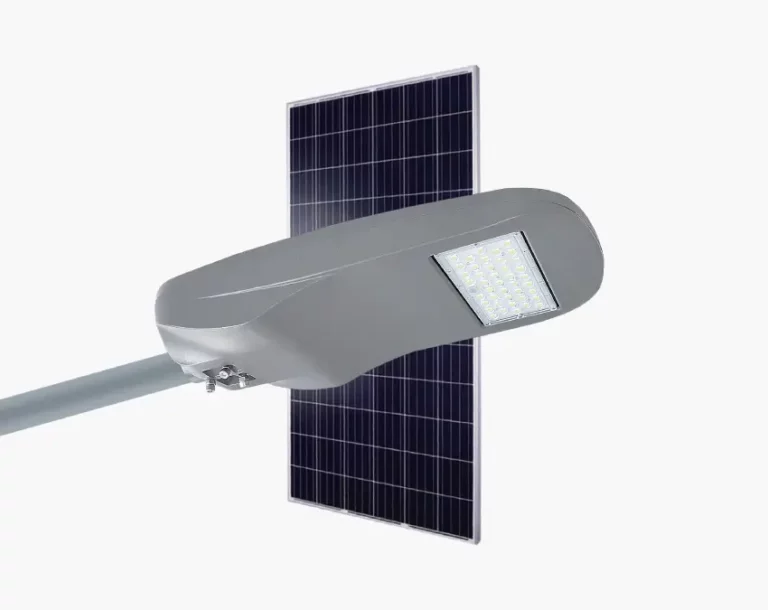
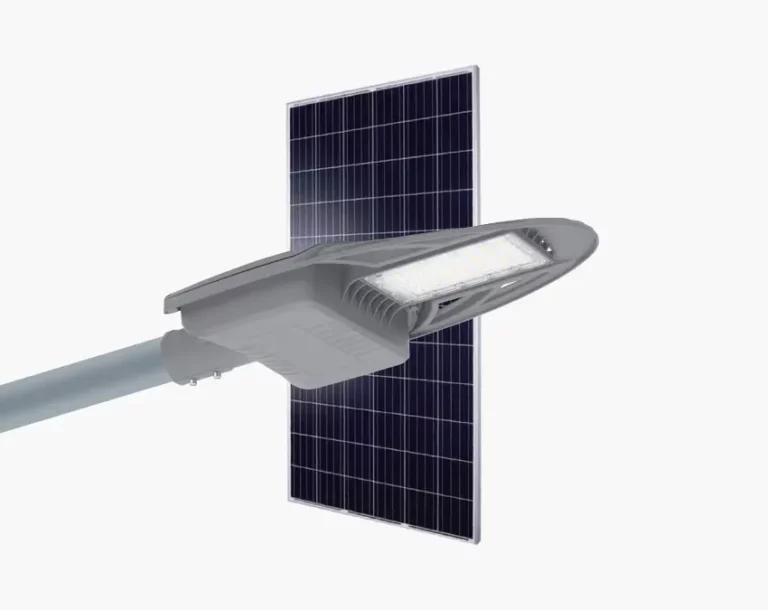
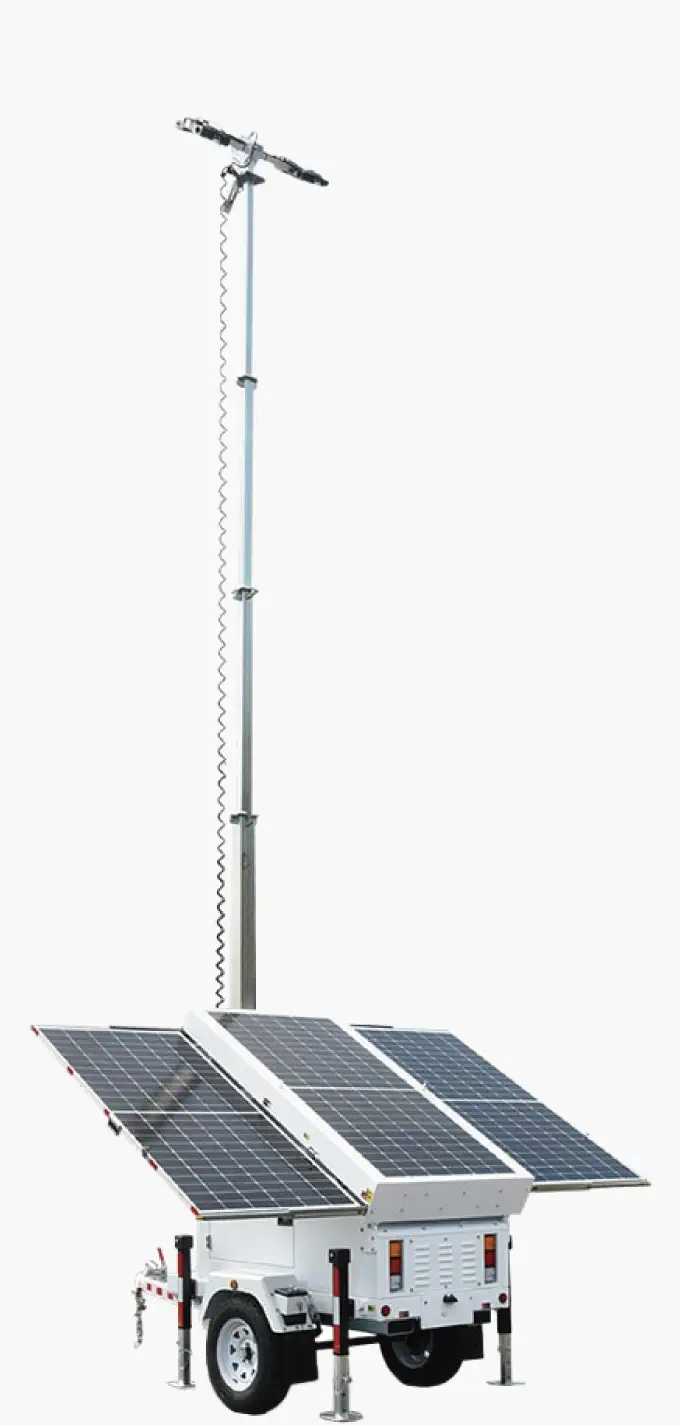
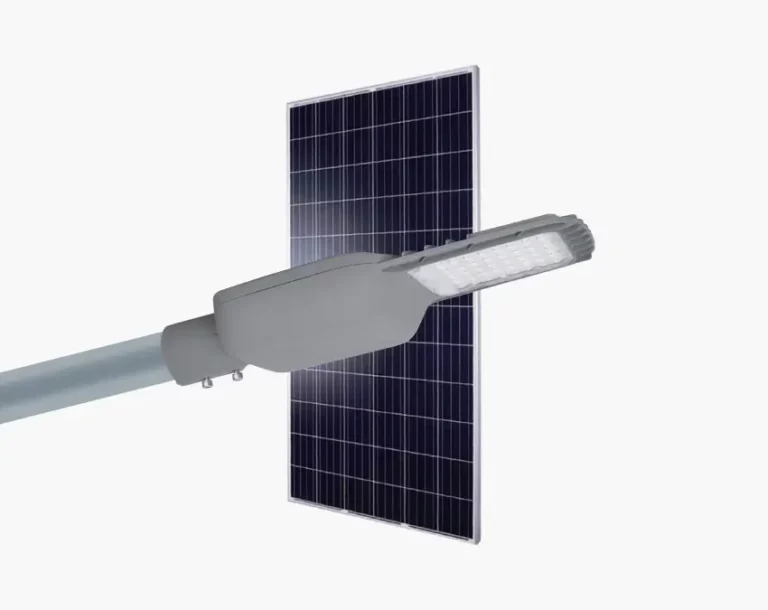
The Chinese company Inlux Solar operates as a leading manufacturer which produces outdoor lighting and traffic management solutions. Inlux operates from a modern 280,000㎡ facility where they manufacture durable traffic light poles that provide stability. Hot-dip galvanized poles from the company can operate reliably in all conditions because they resist winds that exceed 30m/s. Quality infrastructure maintenance requires strong traffic poles because their structural integrity prevents accidents and malfunctions at intersections.
The core business of Inlux Solar revolves around its solar-powered streetlights while also producing traffic light poles. The sustainable lighting system provides dependable illumination to urban and rural locations through self-powered operation. The solar streetlights produced by Inlux are perfect for locations without adequate power supply since they unite innovative technology and energy consumption-efficient features with the capability to make roads and public areas safer through bright illumination. Inlux stands as a reliable partner for infrastructure projects because they specialize in solar lighting systems.
The Growing Importance of Sustainable Power in Traffic Systems
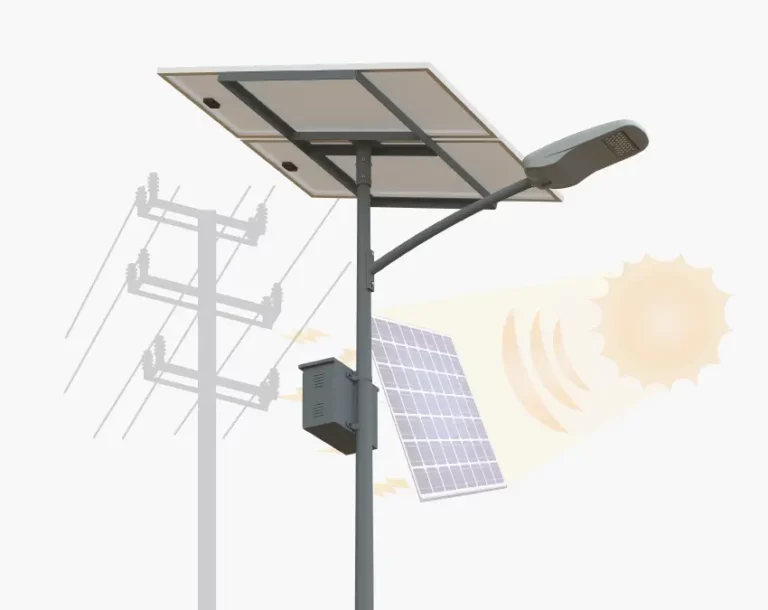
With more focus being placed on sustainability, the need to incorporate renewable energy in infrastructure projects is even more important today. Traffic light systems, which are conventionally powered by the electrical grid, can certainly be designed to incorporate sustainable practices. Inlux Solar not only specializes in the production of robust traffic light poles, but also serves as one of the principal producers of solar powered street lights, having the ability to provide complete solar lighting solutions for cities and villages alike.
Inlux Solar stands by their high quality standards even when it comes to their solar powered products. They incorporate Grade A solar cells and brand new LiFePO4 batteries in their street lights which guarantees over 10 years of service life with 4,000 cycles. Their ultra bright LEDs possess the ability to provide more than 40% additional brightness while having a lifespan over 50,000 hours making them energy efficient and reliable. The company’s focus on these components along with self-reliant power systems makes Inlux a leader towards more eco-friendly and durable traffic management infrastructure. Furthermore, Inlux’s smart solar controllers with multi-protection functions enhance operational efficiency and reliability to a great extent. Traffic signals powered by Inlux’s solutions work reliably and contribute to safer and greener transportation networks.
Conclusion
The dimensions of traffic lights is not an unimportant issue. It is a combination of many things like what type of traffic signal it is, what is the size of the road, what level of traffic visibility is needed, and what the local laws are. Everything from the standard measurement of common vehicle signals to pedestrian, bike, and bus lights are designed with a specific intention to enhance the safety and effectiveness of the transportation network.
Equally important is the support infrastructure for these signals. Inlux Solar,for example, manufactures traffic light poles using renewable energy and is dedicated to offering additional support for the effective and durable infrastructure traffic management systems needed all over the world. Knowing the parameters of traffic lights and their support infrastructure is astonishing. It illustrates the considerable amount of design and engineering effort required to control movement in urban and non urban environments which is increasingly getting more complex.